 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Can various stretches be beneficial for individuals dealing with wrist and hand pain by reducing pain and discomfort to the extremities? Introduction In a technological-driven world, it is common for people to experience wrist and hand pain at some point in their lives. The hands are part of the body’s upper extremities and are used for various tasks and chores throughout the entire day. The forearms provide a causal relationship with the hands and wrists for the upper extremities since they offer very important motor functions to the body. The hands support the body when carrying something; the various muscles, ligaments, tendons, and joints help the wrist with mobility and flexibility. However, when injuries or everyday movements begin to affect the forearms and cause issues with the hands and wrist, it can be difficult to do simple tasks and negatively impact a person’s way of life. Fortunately, numerous ways exist to reduce the pain and discomfort of the wrist and hands. Today’s article focuses on what causes wrist and hand pain, how to prevent wrist and hand pain from returning, and how incorporating various can help reduce the pain-like effects. We discuss with certified medical providers who consolidate our patients’ information to assess the multiple causes that lead to the development of wrist and hand pain. We also inform and guide patients on how various stretches and techniques can help reduce the chances of wrist and hand pain from returning. We also encourage our patients to ask their associated medical providers many intricate and important questions about incorporating these stretches and techniques into their daily routines to live healthier lives. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer. What Causes Hand and Wrist Pain? Do you often feel pain or stiffness in your wrist after typing all day on the computer or phone? Do you have trouble gripping items in your hands? Or how often do your hands ache that massaging them causes temporary relief? Many people, including older adults, have experienced pain at some point, and most of the time, it affects the hands and wrists. Since everyone uses their hands and wrists when performing various tasks, when injuries or repetitive movements start to affect the hands and wrists, it can have a huge impact on simple tasks. When dealing with wrist and hand pain, it can make life unbearable for the person. Since pain is a normal protective response to any injuries and potentially harmful stimuli in its acute form, when prolonged or dysfunctional neuromuscular issues start to affect the body, it may contribute to disability and pain. (Merkle et al., 2020) For wrist and hand pain, many occurrences that lead to its development result from micro-stress or repetitive tear usage. This is because since the world is technological-driven, many people are using computers or smartphones to communicate with each other, which can be one of the causes of the development of wrist and hand pain. When many people frequently use electronic devices, the frequent movements and uses of the thumbs will increase their load and become a higher prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders. (Baabdullah et al., 2020) Other studies stated that when many individuals begin to do repetitive movements constantly and have different positions of their wrist joints while using their electronic devices continually, it can cause pain to their wrist joints and affect the structure. (Amjad et al., 2020) Additionally, when repetitive vibration exposures or forceful angular motions affect the hands and wrists, it can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome and affect the hands. (Osiak et al., 2022) The various joints, tendons, and muscles also become affected in the hands and wrist as trigger points in the forearm. Fortunately, there are multiple ways that many people can reduce the pain-like effects of wrist and hand pain. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
For individuals looking to improve their fitness health, can a fitness assessment test identify potential areas and help evaluate overall health and physical status? Fitness Assessment A fitness test, also known as a fitness assessment, helps evaluate an individual's overall and physical health. It comprises a series of exercises to design an appropriate exercise program for general health and fitness. (National Strength and Conditioning Association. 2017) Fitness assessment testing benefits include: - Identifying areas that need improvement.
- Assisting professionals in understanding what types of exercise are safest and most effective.
- Helping measure fitness progress over time.
- Allowing for an individualized plan that can help prevent injuries and maintain the body's overall health.
An assessment can comprise a wide range of tests, including: - Body composition tests.
- Cardiovascular stress tests.
- Endurance tests.
- Range of motion tests.
They are meant to ensure the individual won't be at risk of injury and provide the trainer with the insights needed to establish clear and effective fitness goals. Individuals who wonder whether fitness testing would benefit them should consult their healthcare provider. General Health Before starting a fitness program, it is important to inform the trainer of individual medical history and get the necessary approval from a primary healthcare provider. (Harvard Health Publishing. Harvard Medical School. 2012) Fitness specialists usually use one or more screening tools to help determine individual baseline health.
This may include obtaining vital sign measurements like height and weight, resting heart rate/RHR, and resting blood pressure/RBP. Many trainers will also use a physical activity readiness questionnaire/PAR-Q comprising questions about general health. (National Academy of Sports Medicine. 2020) Among the questions, individuals may be asked about the medications being taken, any problems with dizziness or pain, or medical conditions that may impair their ability to exercise.
Body Composition Body composition describes total body weight components, including muscles, bones, and fat. The most common methods for estimating body composition include: Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis - BIA - During BIA, electrical signals are sent from electrodes through the soles of the feet to the abdomen to estimate body composition. (Doylestown Health. 2024)
Body Mass Index - BMI Skinfold Measurements - These measurements use calipers to estimate the amount of body fat in a fold of skin.
Cardiovascular Endurance Cardiovascular endurance testing, also known as stress testing, measures how efficiently the heart and lungs work to supply oxygen and energy to the body during physical activity. (UC Davis Health, 2024) The three most common tests used include: 12-minute Run Tests - Twelve-minute run tests are performed on a treadmill, and an individual's pre-exercise heart and respiration rates are compared with post-exercise heart and respiration rates.
Exercise Stress - Exercise stress testing is performed on a treadmill or stationary bike.
- It involves using a heart monitor and blood pressure cuff to measure vital signs during exercise.
VO2 Max Testing - Performed on a treadmill or stationary bike.
- V02 max testing uses a breathing device to measure the maximum rate of oxygen consumption during physical activity (UC Davis Health, 2024)
- Some trainers will incorporate exercises like sit-ups or push-ups to measure response to specific exercises.
- These baseline results can be used later to see if health and fitness levels have improved.
Strength and Endurance Muscle endurance testing measures the length of time a muscle group can contract and release before it fatigues. Strength testing measures the maximal amount of force a muscle group can exert. (American Council on Exercise, Jiminez C., 2018) The exercises used include: - The push-up test.
- Core strength and stability test.
Sometimes, a trainer will use a metronome to measure how long the individual can keep up with the rhythm. The results are then compared to individuals of the same age group and sex to establish a baseline level. Strength and endurance tests are valuable as they help the trainer spot which muscle groups are stronger, vulnerable, and need focused attention. (Heyward, V. H., Gibson, A. L. 2014). Flexibility - Measuring the flexibility of joints is vital in determining whether individuals have postural imbalances, foot instability, or limitations in range of motion. (Pate R, Oria M, Pillsbury L, 2012)
Shoulder Flexibility - Shoulder flexibility testing evaluates the flexibility and mobility of the shoulder joint.
- It is performed by using one hand to reach behind the neck, between the shoulders, and the other hand to reach behind the back, toward the shoulders, to measure how far apart the hands are. (Baumgartner TA, PhD, Jackson AS, PhD et al., 2015)
Sit-And-Reach - This test measures tightness in the lower back and hamstring muscles. (American Council of Exercise, Metcalf A. 2014)
- The sit-and-reach test is performed on the floor with the legs fully extended.
- Flexibility is measured by how many inches the hands are from the feet when reaching forward.
Trunk Lift - Trunk lift testing is used to measure tightness in the lower back.
- It is performed while lying face-down on the floor with arms at your side.
- The individual will be asked to lift their upper body with just the back muscles.
- Flexibility is measured by how many inches the individual can lift themselves off the ground. (Baumgartner TA, PhD, Jackson AS, PhD et al., 2015)
Fitness assessment testing has various benefits. It can help trainers design a personalized workout program, help individuals identify fitness areas that need improvement, measure progress, and add intensity and endurance to their routine, which can help prevent injuries and help maintain overall health. We focus on what works for you and strive to better the body through researched methods and total wellness programs. These natural programs use the body’s ability to achieve improvement goals. Ask a healthcare professional or fitness professional for guidance if you need advice. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References National Strength and Conditioning Association. (2017). Purposes of assessment. https://www.nsca.com/education/articles/kinetic-select/purposes-of-assessment/ Harvard Health Publishing. Harvard Medical School. (2012). Do you need to see a doctor before starting your exercise program? HealthBeat. https://www.health.harvard.edu/healthbeat/do-you-need-to-see-a-doctor-before-starting-your-exercise-program National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2020). PAR-Q-+ The Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire for Everyone. https://www.nasm.org/docs/pdf/parqplus-2020.pdf?sfvrsn=401bf1af_24 Doylestown Health. (2024). Bio-Electrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)-Body Mass Analysis. https://www.doylestownhealth.org/service-lines/nutrition#maintabbed-content-tab-2BDAD9F8-F379-403C-8C9C-75D7BFA6E596-1-1 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (N.D.). Calculate your body mass index. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/BMI/bmicalc.htm UC Davis Health. (2024). VO2max and Aerobic Fitness. https://health.ucdavis.edu/sports-medicine/resources/vo2description American Council on Exercise. Jiminez C. (2018). Understanding 1-RM and Predicted 1-RM Assessments. ACE Fitness. https://www.acefitness.org/fitness-certifications/ace-answers/exam-preparation-blog/2894/understanding-1-rm-and-predicted-1-rm-assessments/
Heyward, V. H., Gibson, A. L. (2014). Advanced Fitness Assessment and Exercise Prescription. United Kingdom: Human Kinetics. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Advanced_Fitness_Assessment_and_Exercise/PkdoAwAAQBAJhl=en&gbpv=1&dq=Strength+and+endurance+tests+muscle+groups+are+stronger+and+weaker&pg=PA173&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=Strength%20and%20endurance%20tests%20muscle%20groups%20are%20stronger%20and%20weaker&f=false
Pate R, Oria M, Pillsbury L, (Eds). (2012). Health-related fitness measures for youth: Flexibility. In R. Pate, M. Oria, & L. Pillsbury (Eds.), Fitness Measures and Health Outcomes in Youth. https://doi.org/10.17226/13483 Baumgartner, T. A., Jackson, A. S., Mahar, M. T., Rowe, D. A. (2015). Measurement for Evaluation in Kinesiology. United States: Jones & Bartlett Learning. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Measurement_for_Evaluation_in_Kinesiolog/_oCHCgAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=1&dq=Measurement+for+Evaluation+in+Kinesiology+(9th+Edition).&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false American Council of Exercise. Metcalf A. (2014). How to improve flexibility and maintain it. ACE Fitness. https://www.acefitness.org/resources/everyone/blog/3761/how-to-improve-flexibility-and-maintain-it/
Can improving breathing patterns help further fitness and optimize overall health for individuals who walk for exercise? Improve Breathing and Walking Exercising is a moment in which breathing can quicken and become labored if not done correctly. There is a proper way to breathe when exercising, especially when walking or speed walking. Breathing incorrectly causes rapid fatigue and exhaustion. Controlling the flow of one's breath improves endurance and cardiovascular health, and it can also amplify metabolism, mood, and energy levels. (Hsiu-Chin Teng et al., 2018) Known as diaphragmatic breathing, it is used for those with reduced lung capacity, like individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/COPD. The practice improves lung capacity and is a recommended way to help relieve stress. Physiology - During exercise, the oxygen inhaled converts the calories consumed into energy that fuels the body. This process is referred to as metabolism.
- When the oxygen supply exceeds the body's oxygen needs, the body is in an aerobic state. This means there is plenty of oxygen to fuel physical activity/exercise as there are calories to burn.
- If the oxygen supply falls short of the body's oxygen needs, the body falls into an anaerobic state.
- Deprived of oxygen, the body turns to stored fuel in the muscles, known as glycogen.
- This delivers a powerful burst of energy, but the fuel is quickly spent and fatigue and exhaustion soon follow.
- Increasing airflow in and out of the lungs can prevent early exhaustion and help the body burn calories more effectively. (Your lungs and exercise. Breathe 2016)
Improved Breathing Benefits Optimal breathing starts in infancy. When a baby breathes, their belly rises and falls. This facilitates respiration by pushing and pulling the diaphragm - the muscle that separates the lungs and abdominal cavity. When the baby inhales, the belly extends, pulling the diaphragm downward and allowing the lungs to fill with air. When the baby exhales, the belly draws in, pressing the diaphragm upward and forcing air out. As the body ages and the capacity of the lungs increases, individuals shift from belly-breathing to chest-breathing. Chest breathing involves the chest wall muscles with little use of the diaphragm. Chest breathing usually provides enough air for everyday activity but does not fill the lungs. This is why individuals resort to mouth-breathing or gasping when the oxygen supply is limited. Even those in decent physical shape may be inadvertently undermining efforts by sucking in their stomach to look thinner, depriving themselves of complete inhalations and exhalations. To overcome this, individuals need to re-train their bodies to activate the abdominal muscles when walking. Belly or diaphragmatic breathing can extend the duration of exercise while strengthening the core muscles. (Nelson, Nicole 2012) By increasing core stability, individuals can better support the spine and maintain a healthy posture when walking. This stabilizes the hips, knees, upper back, and shoulders, making the body less prone to strain, instability, and fatigue from unhealthy posture. (Tomas K. Tong et al., 2014) Breathing Correctly The inhalation draws the belly out, pulls the diaphragm down, and inflates the lungs. Simultaneously, it extends the ribcage and lengthens the lower spine. This forces the shoulders and collarbone backward, further opening the chest. Exhaling does the reverse. Walking Start by inhaling and exhaling through the nose, ensuring that the inhalation duration matches the exhalation duration. When picking up the pace, individuals can resort to mouth-breathing, maintaining the same inhalation/exhalation rhythm. At no time should breathing be held in. Learning diaphragmatic breathing takes time, but the following steps can be a starting point: - Inhale by inflating the belly fully on a count of five.
- Allow the lungs to fill, drawing the shoulders back as this happens.
- Exhale by pulling the belly button toward the spine on a count of five.
- Use the diaphragm to press the air out of the lungs, keeping the spine erect.
- Repeat.
If unable to maintain a count of five, individuals can shorten the count or slow the pace of the walk. Individuals in good shape can extend the count. Initially, diaphragmatic breathing may not come naturally, but it will become automatic with practice. Stop and place your hands over your head if you are short of breath when walking. Breathe in and out deeply and evenly until breathing returns to normal. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Teng, H. C., Yeh, M. L., & Wang, M. H. (2018). Walking with controlled breathing improves exercise tolerance, anxiety, and quality of life in heart failure patients: A randomized controlled trial. European journal of cardiovascular nursing, 17(8), 717–727. https://doi.org/10.1177/1474515118778453 Your lungs and exercise. (2016). Breathe (Sheffield, England), 12(1), 97–100. https://doi.org/10.1183/20734735.ELF121 Tong, T. K., Wu, S., Nie, J., Baker, J. S., & Lin, H. (2014). The occurrence of core muscle fatigue during high-intensity running exercise and its limitation to performance: the role of respiratory work. Journal of sports science & medicine, 13(2), 244–251. Nelson, Nicole MS, LMT. (2012). Diaphragmatic Breathing: The Foundation of Core Stability. Strength and Conditioning Journal 34(5):p 34-40, October 2012. | DOI: 10.1519/SSC.0b013e31826ddc07
For individuals experiencing musculoskeletal issues and pain symptoms, can learning about biomechanics and how it applies to movement, physical training, and performance, help in injury treatment and prevention? Biomechanics Biomechanics studies all life forms and their mechanical workings. Many think of biomechanics in sports and athletic performance, but biomechanics helps create and improve technologies, equipment, and injury rehabilitation techniques. (Tung-Wu Lu, Chu-Fen Chang 2012) Scientists, sports medicine doctors, physiotherapists, chiropractors, and conditioning specialists utilize biomechanics to help develop training protocols and techniques to improve therapy outcomes. Body Movement Biomechanics studies the movement of the body, including how muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments work together, especially when movement is not optimal or correct. It is part of the larger field of kinesiology, specifically focusing on motion mechanics and analysis of how all the individual parts of the body work together to make up athletic and normal movements. (José M Vilar et al., 2013) Biomechanics includes: - Structure of bones and muscles.
- Movement ability.
- Mechanics of blood circulation, renal function, and other functions.
- The study of forces and the effects of these forces on the tissues, fluid, or materials used for diagnosis, treatment, or research. (Jose I. Priego-Quesada 2021)
Sports Sports biomechanics studies motion in exercising, training, and sports, which incorporates physics and the laws of mechanics. For example, the biomechanics of a specific exercise looks at: - Body position.
- Movement of the feet, hips, knees, back, shoulders, and arms.
Knowing the correct movement patterns helps make the most of the exercise while preventing injuries, correcting form mistakes, informing training protocols, and increasing positive results. Understanding how the body moves and why it moves the way it does helps medical professionals prevent and treat injuries, alleviate pain symptoms, and improve performance. Equipment Biomechanics is used in the development of physical and sports equipment to improve performance. For example, a shoe can be designed for optimal performance for a skateboarder, long-distance runner, or soccer player. Playing surfaces are also studied for this purpose, such as how the surface stiffness of artificial turf affects athletic performance. (Jose I. Priego-Quesada 2021) Individuals - Biomechanics can analyze an individual's movements for more effective movement during training and games.
- For example, an individual’s running gait or swing can be filmed with recommendations on what to change to improve.
Injuries - The science studies the causes, treatment, and prevention of neuromusculoskeletal injuries.
- The research can analyze the forces that cause injuries and provide information for medical professionals on how to reduce the risk of injury.
Training - Biomechanics studies sports techniques and training systems to develop ways to improve efficiency.
- This can include research on positioning, release, follow-through, etc.
- It can analyze and help design new training techniques based on the mechanical demands of the sport, aimed at resulting in better performance.
- For example, muscle activation is measured in cycling using electromyography and kinematics, which helps researchers analyze factors like posture, components, or exercise intensity that affect activation. (Jose I. Priego-Quesada 2021)
Motions In biomechanics, the body's motions are referred to from anatomical positioning: - Standing upright, with the gaze straight ahead
- Arms at the sides
- Palms facing forward
- Feet spaced slightly apart, toes forward.
The three anatomical planes include: - Sagittal - median - Dividing the body into right and left halves is the sagittal/median plane. Flexion and extension occur in the sagittal plane.
- Frontal - The frontal plane divides the body into front and back sides but also includes abduction, or moving a limb away from the center, and adduction, or moving a limb towards the center in the frontal plane.
- Transverse - horizontal. - The upper and lower parts of the body are divided by the transverse/horizontal plane. Rotating movements occur here. (American Council on Exercise 2017)
- Moving the body in all three planes occurs with daily activity. This is why performing exercises in each plane of motion to build strength, function, and stability is recommended.
Tools Various tools are used to study biomechanics. Studies are usually performed using a device known as electromyography or EMG sensors. Sensors are placed on the skin and measure the amount and degree of muscle fiber activation in certain muscles during test exercises. EMGs can help: - Researchers understand which exercises are more effective than others.
- Therapists know whether patients' muscles are properly operating and functioning.
- Dynamometers are another tool that helps measure muscle strength.
- They measure the force output generated during muscle contractions to see if the muscles are sufficiently strong.
- They are used to measure grip strength, which can be an indicator of overall strength, health, and longevity. (Li Huang et al., 2022)
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Lu, T. W., & Chang, C. F. (2012). Biomechanics of human movement and its clinical applications. The Kaohsiung journal of medical sciences, 28(2 Suppl), S13–S25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2011.08.004 Vilar, J. M., Miró, F., Rivero, M. A., & Spinella, G. (2013). Biomechanics. BioMed research international, 2013, 271543. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/271543 Priego-Quesada J. I. (2021). Exercise Biomechanics and Physiology. Life (Basel, Switzerland), 11(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020159 American Council on Exercise. Makeba Edwards. (2017). Planes of Motion Explained (Exercise Science, Issue. https://www.acefitness.org/fitness-certifications/ace-answers/exam-preparation-blog/2863/the-planes-of-motion-explained/ Huang, L., Liu, Y., Lin, T., Hou, L., Song, Q., Ge, N., & Yue, J. (2022). Reliability and validity of two hand dynamometers when used by community-dwelling adults aged over 50 years. BMC geriatrics, 22(1), 580. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-03270-6
For individuals looking to improve overall health and wellness, how can paying attention to non-exercise activities help burn more calories and improve metabolic rates? Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis - NEAT Non-exercise activity thermogenesis, or NEAT, describes the calories burned by daily movements and activities. These physical movements are not planned or structured exercises, workouts, or sports. It is also referred to as non-exercise physical activity or NEPA. Examples include activities like: - Cleaning
- Cooking
- Shopping
- Playing a musical instrument
- Small movements like fidgeting
- When buying a few items, carry a basket instead of a shopping cart.
- Take the stairs instead of the elevator or escalator.
While these movements might not seem like a lot, they can have a substantial impact on metabolic rates and calorie expenditures. A study followed over 12,000 women for 12 years and found that fidgeting can reduce the risk of death associated with excessive sedentariness. (Gareth Hagger-Johnson et al., 2016) Calories Burned The amount of calories burned varies from person to person. A study reported that the number of calories burned from non-exercise activity thermogenesis varies up to 2000 kilocalories a day between two individuals of similar size. (Christian von Loeffelholz et al., 2000). A number of factors can account for this difference, including environment and genetics. Individuals' occupations and lifestyles can also influence non-exercise activity thermogenesis. For example, two individuals with similar body mass indexes or BMIs but different jobs, sedentariness versus activity, will burn different calorie amounts. Improving Health Non-exercise activity thermogenesis is thought to be one of the ways the body manages weight. When gaining weight, NEAT tends to increase, whereas when losing weight, NEAT decreases with individuals sitting more without moving as much. A research review noted that the benefits of non-exercise go well beyond the extra calories expended. (Pedro A. Villablanca et al., 2015). Increasing non-exercise activity thermogenesis reduces the risk of metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular issues, and other health problems. Plus, research shows that inactivity can negate the time and effort put into structured exercise. (John D. Akins et al., 2019). Combating sedentary behavior with non-activity thermogenesis helps increase the benefits of regular workouts. Incorporating NEAT There are small ways to incorporate non-exercise activity thermogenesis at work and home. This could be using a standing desk or stability ball. According to the National Academy of Sports Medicine, a 145-pound person can approximately burn: - 102 calories an hour while sitting at work.
- 174 calories if standing at work.
- 72 calories extra may not seem like a lot, but it can add up to more than 18,000 calories burned per year, leading to an approximate 5-pound weight loss.
If waiting in line or sitting in traffic, finding small ways to move, like tapping the hands or feet or moving the head to music, helps the body take advantage of non-exercise activity thermogenesis. Making more conscious efforts to move can go a long way in improving health. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Hagger-Johnson, G., Gow, A. J., Burley, V., Greenwood, D., & Cade, J. E. (2016). Sitting Time, Fidgeting, and All-Cause Mortality in the UK Women's Cohort Study. American journal of preventive medicine, 50(2), 154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2015.06.025 von Loeffelholz, C., & Birkenfeld, A. L. (2022). Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis in Human Energy Homeostasis. In K. R. Feingold (Eds.) et. al., Endotext. MDText.com, Inc. Villablanca, P. A., Alegria, J. R., Mookadam, F., Holmes, D. R., Jr, Wright, R. S., & Levine, J. A. (2015). Nonexercise activity thermogenesis in obesity management. Mayo Clinic proceedings, 90(4), 509–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.02.001 Akins, J. D., Crawford, C. K., Burton, H. M., Wolfe, A. S., Vardarli, E., & Coyle, E. F. (2019). Inactivity induces resistance to the metabolic benefits following acute exercise. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 126(4), 1088–1094. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00968.2018
For older individuals experiencing posture problems, slumping, slouching, and upper back pain, could adding rib cage exercises help bring relief and prevent the condition from worsening? Improved Posture It's common to associate a collapsed upper back posture with age, but other factors can also contribute to the problems. (Justyna Drzał-Grabiec, et al., 2013) The rib cage and the pelvis are important to body structure and comprise much of the core. If these bone structures become misaligned due to unhealthy posture, the muscles that attach to them become tight, weak, or both, and the surrounding muscles have to compensate, causing a worsening of the condition and further injury. - Unhealthy postures can be caused by a rib cage that compresses down onto the pelvic bone.
- As the upper back slumps or compresses, height can begin to decrease.
- Posture awareness exercises can help lift the rib cage off the pelvic bone.
Rib Cage Exercises This exercise can be done sitting or standing. A daily routine can help improve posture and relieve back problems and pain. - The sitting version helps keep the focus on doing the exercise right.
- The standing version challenges body awareness, allowing the individual to feel how the rib cage and upper back movements affect pelvic and lower back posture.
- To begin, it is recommended to start in a sitting position.
- Once the basics are learned, then certainly progress to standing.
Exercise - Position the pelvis so it is in a slight forward tilt.
- This forward tilt will exaggerate the low back curve slightly while tightening the lower back muscles in a good way.
- Establishing and maintaining this curve in the sitting position should feel natural.
- Inhale and exaggerate the upward lift of the rib cage.
- Inhaling causes the spine and ribs to extend slightly.
- Exhale and allow the rib cage and upper back to return to their natural position.
- Repeat up to 10 times once or twice a day.
- For this exercise, use breathing to develop the rib cage's lift and carriage incrementally.
- Don't max out on the spinal extension.
- Instead, focus on how breathing/inhaling supports the movement of the ribs and upper back and develops the muscles from there.
- Try to lift the rib cage equally on both sides as the body allows.
With practice, individuals will realize the healthy posture changes and increased distance between the ribs and pelvis. Guidance and Variation - Perform the exercise with the back against a wall for upper back guidance.
- Another variation of the pelvis and rib cage posture training exercise is to raise the arms.
- This will create a different posture awareness training perspective.
- Focus on rib cage movement when the arms are raised.
- Does lifting the arms make the exercise easier, harder, or different?
- To enhance posture improvement, stretch the pectoral muscles.
Yoga Individuals looking for more ways to strengthen healthy posture should consider yoga. A study published in the International Journal of Yoga suggests that a great way to activate the core may be to include a variety of yoga postures into the routine. (Mrithunjay Rathore et al., 2017) The ab muscles attach to various places on the rib cage and play a role in posture, alignment, and balance. The researchers identified two muscles, the external obliques, and the transverse abdominal, as key to a healthily aligned posture. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Drzał-Grabiec, J., Snela, S., Rykała, J., Podgórska, J., & Banaś, A. (2013). Changes in the body posture of women occurring with age. BMC geriatrics, 13, 108. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2318-13-108 Rathore, M., Trivedi, S., Abraham, J., & Sinha, M. B. (2017). Anatomical Correlation of Core Muscle Activation in Different Yogic Postures. International journal of yoga, 10(2), 59–66. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6131.205515 Papegaaij, S., Taube, W., Baudry, S., Otten, E., & Hortobágyi, T. (2014). Aging causes a reorganization of cortical and spinal control of posture. Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 6, 28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00028
Individuals that engage in a regular fitness regimen can begin to lose interest and motivation. Can knowing the signs of exercise burnout help individuals rediscover their motivation? Exercise Burnout When maintaining fitness and health becomes a chore and doing anything else is better than working out, individuals could be experiencing exercise burnout. Here are a few signs an individual is getting burned out. Procrastination One sign is constantly putting things off. - An individual may put on workout clothes, set up the equipment, etc.
- However, the workout never happens as the individual continues to find other things to do.
- At some point, they decide it's too late and they'll work out tomorrow.
Solution Simplify the workout. Make some small goals or adjustments and keep the workout light. (Nemanja Lakicevic, et al., 2020) An example could be: - Focus only on stretching.
- Take a walk around the block.
- Go up and down some stairs equivalent of a few laps.
- Do 10 pushups, 10 squats, and 10 lunges, or other exercises and that's it.
No Longer Interesting When burned out, exercise is not interesting and disenchanting. (Franklin Velasco, Rafael Jorda. 2020) Trainers will suggest finding something positive about the workouts. Solution Switch to a new or different activity. (Nemanja Lakicevic, et al., 2020) - When the interest and passion are nowhere to be found don't engage in the usual workouts, as this can further decrease motivation.
- This is the time to change up the routine and go for a leisurely bicycle or rollerblade, skateboard, etc., session.
- Go to a park, just walk around, and forget about exercise just taking in everything.
- Play a game with a friend or toss a ball around.
Exhaustion Not just physical, but mental fatigue could be a sign of exercise burnout. Solution - Rest.
- Individuals may think they have to work out every day and stick to the regimen or else they've failed.
- This type of mindset can lead to burnout and added stress.
- The body and mind require adequate recovery time.
- Forget about structured exercise for a day, and see how the mind and body feel the next day.
- Two or three days off in a row can make a significant difference in motivation and offer a new perspective on the workout routine.
Low Energy Levels After Exercise Workouts, although tiring in a good way, should energize the individual. Most workouts should leave the body feeling better than before. When the body feels worse or energy levels are low, this could be a sign of overtraining that could lead to exercise burnout. Solution - This could be the time to ease off of the fitness regimen.
- Forget intense workouts and/or heavy-weight training.
- This is the time to soothe the body.
- Light yoga workouts or Pilates could help.
- This is a form of active recovery, allowing the mind and body to rest from the overwork.
Mood Changes and/or Irritability When the mind and body are overworked and over-trained, it can cause moodiness, irritability, and frustration that leads to burnout. Solution Do something that feels good. This could include: - A therapeutic massage.
- A spa session.
- Taking a long nap.
- Soaking the feet.
- Taking a therapeutic bath.
- Meditation
Burnout can happen, the objective is to keep the solutions simple like taking a few days off or trying something new to come back feeling refreshed and energized. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Lakicevic, N., Gentile, A., Mehrabi, S., Cassar, S., Parker, K., Roklicer, R., Bianco, A., & Drid, P. (2020). Make Fitness Fun: Could Novelty Be the Key Determinant for Physical Activity Adherence?. Frontiers in psychology, 11, 577522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.577522 Velasco, F., & Jorda, R. (2020). Portrait of Boredom Among Athletes and Its Implications in Sports Management: A Multi-Method Approach. Frontiers in psychology, 11, 831. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00831
Gender transitioning is the process of affirming and expressing an individual's internal sense of gender rather than the one assigned at birth. How can learning the aspects of gender and gender transitioning help support the LGBTQ+ community? Gender Transitioning Gender transitioning or gender affirmation is a process through which transgender and gender-nonconforming individuals align their internal gender identity with their external gender expression. It can be described as a binary - male or female - but can also be non-binary, meaning an individual is neither exclusively male nor female. - The process can involve aesthetic appearances, changes in social roles, legal recognitions, and/or physical aspects of the body.
- Social affirmation - dressing differently or coming out to friends and family.
- Legal affirmation - changing name and gender on legal documents.
- Medical affirmation - using hormones and/or surgery to change certain physical aspects of their body.
- Transgender individuals can pursue some or all of these.
Barriers Gender transitioning can be obstructed by various barriers that can include: - Cost
- Lack of insurance
- Lack of family, friends, or partner support.
- Discrimination
- Stigma
Addressing All Aspects The process does not have a specific timeline and is not always linear. - Many transgender and gender-nonconforming individuals prefer gender affirmation to gender transitioning because transitioning is often taken to mean the process of medically transforming the body.
- An individual does not have to undergo medical treatment to affirm their identity, and some transgender people avoid hormones or gender-affirming surgery.
- Transitioning is a holistic process that addresses all aspects of who a person is inwardly and outwardly.
- Certain aspects of transitioning may be more important than others, like changing one's name and gender on their birth certificate.
- Reevaluation and revision of gender identity can be continual rather than a step-by-step, one-way process.
Exploring Gender Identity Gender transitioning often starts in response to gender dysphoria which describes the constant sense of uneasiness that occurs when the gender an individual was assigned at birth does not match how they experience or express their gender internally. - Some individuals have experienced symptoms of gender dysphoria as early as 3 or 4 years of age. (Selin Gülgöz, et al., 2019)
- Gender dysphoria can be largely informed by the culture that surrounds the individual, specifically in cultures where strict codes determine what is masculine/male and feminine/female.
Unease Expressed in Different Ways - Dislike of one’s sexual anatomy.
- A preference for clothes typically worn by the other gender.
- Not wanting to wear clothes typically worn by their own gender.
- A preference for cross-gender roles in fantasy play.
- A strong preference for engaging in activities that are typically done by the other gender.
Dysphoria - Gender dysphoria can fully emerge during puberty when awareness about how an individual's body defines them creates internal distress.
- Feelings may be amplified when an individual is described as a tomboy, or a sissy, or is criticized and attacked for acting like a girl or acting like a boy.
- During puberty, the physical changes can cause long-standing feelings of not fitting in and may evolve into feelings of not fitting in their own body.
- This is when individuals can undergo a process referred to as internal transitioning and begin to change how they see themselves.
Gender transitioning/affirmation becomes the next step. Transitioning is not about changing or recreating oneself but about expressing their authentic self and asserting who they are socially, legally, and/or medically. Social Social transitioning involves how a person publicly expresses their gender. The transition can include: - Changing pronouns.
- Using chosen name.
- Coming out to friends, family, coworkers, etc.
- Wearing new clothes.
- Cutting or styling hair differently.
- Changing mannerisms like moving, sitting, etc.
- Changing voice.
- Binding - strapping the chest to hide breasts.
- Wearing breast and hip prosthetics to accentuate feminine curvature.
- Packing - wearing a penile prosthesis to create a penile bulge.
- Tucking - tucking the penis to conceal a bulge.
- Playing certain sports
- Pursuing different lines of work.
- Participating in activities that might typically be seen as male or female.
Legal Legal transitioning involves changing legal documents to reflect the individual's chosen name, gender, and pronouns. This includes governmental and non-government documents that can include: - Birth certificates
- Social Security ID
- Driver's license
- Passport
- Bank records
- Medical and dental records
- Voter registration
- School ID
- Provisions allowing for changes can vary by state.
- Some states only allow changes if bottom surgery - genital reconstruction is performed.
- Others will allow the changes without any form of gender-affirming surgery.
- Other states have begun to offer an X-gender option for non-binary individuals. (Wesley M King, Kristi E Gamarel. 2021)
Medical Medical transitioning typically involves hormone therapy to develop some of the male or female sex characteristics. It can also involve surgery to change certain physical aspects combined with hormone therapy. - Hormone therapy assists individuals to physically look more like the gender they identify as.
- They can be used on their own and can also be used before gender-affirming surgery.
Hormone therapy takes two forms: Transgender Men Transgender Women Surgery Gender affirmation surgery aligns an individual's physical appearance to their gender identity. Many hospitals provide gender-affirming surgery through a transgender medicine department. Medical procedures include: - Facial surgery - Facial feminization surgery.
- Breast augmentation - Increases breast size with implants.
- Chest masculinization - Removes contours of breast tissues.
- Tracheal shaving - Reduces Adam's apple.
- Phalloplasty - Construction of a penis.
- Orchiectomy - Removal of the testicles.
- Scrotoplasty - Construction of a scrotum.
- Vaginoplasty - Construction of a vaginal canal.
- Vulvoplasty - Construction of the outer female genitalia.
Roadblocks If you know someone who is transgender or is considering transitioning, learning about gender and gender transitioning and how to be supportive is a great way to be an ally. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Gülgöz, S., Glazier, J. J., Enright, E. A., Alonso, D. J., Durwood, L. J., Fast, A. A., Lowe, R., Ji, C., Heer, J., Martin, C. L., & Olson, K. R. (2019). Similarity in transgender and cisgender children's gender development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(49), 24480–24485. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1909367116 Irwig, M. S., Childs, K., & Hancock, A. B. (2017). Effects of testosterone on the transgender male voice. Andrology, 5(1), 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12278 Tangpricha, V., & den Heijer, M. (2017). Estrogen and anti-androgen therapy for transgender women. The Lancet. Diabetes & endocrinology, 5(4), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30319-9 National Center for Transgender Equality. Know Your Rights in Health Care. Kaiser Family Foundation. Update on Medicaid coverage of gender-affirming health services. Center of Medicare and Medicaid Services. Gender dysphoria and gender reassignment surgery. Transgender Legal Defense and Education Fund. Health insurance medical policies. National Center for Transgender Equality and National Gay and Lesbian Task Force. Injustice at Every Turn: A Report of the National Transgender Discrimination Survey. Turban, J. L., Loo, S. S., Almazan, A. N., & Keuroghlian, A. S. (2021). Factors Leading to "Detransition" Among Transgender and Gender Diverse People in the United States: A Mixed-Methods Analysis. LGBT health, 8(4), 273–280. https://doi.org/10.1089/lgbt.2020.0437
For athletes, the vertical jump is a skill that can be increased and improved with proper training. To improve jumping abilities for sports like basketball, tennis, volleyball, or track and field events such as the high jump it is necessary to do both strength and power training. Research has found certain key components can help athletes become better at jumping. There are different ways to improve an individual's vertical jump. Here we go over some of the most effective exercises including plyometrics, and exercises that build strength and power. Vertical Jump Increase and Improvement Jumping is an explosive movement. - To jump well, an individual needs a consistent powerful spring.
- This is achieved by training the explosive/fast-twitch muscle fibers with the ability to shorten and stretch dynamically.
- Upper body strength is important for creating upward momentum.
- Strength exercises involve slow, controlled movements like squats, lunges, and step-ups with weights.
- Power exercises involve explosive, quick movements.
- Plyometrics involve explosive hopping, bounding, and jumping drills that combine strength and speed.
Exercises Plyometrics - Common plyometric exercises include hops, jumps, and bounding movements.
- A popular exercise is jumping off a box and rebounding off the floor then jumping onto another, higher box.
- Box jumps provide practice for jumping.
Single-Leg Squats - Single-leg squats can be done almost anywhere, without equipment.
- They work the hips, hamstrings, quadriceps, gluteus maximus, and calves.
- They strengthen the core and increase flexibility.
Full Squats - This is a barbell exercise to build strength and power.
- It is considered one of the best total body exercises.
Weighted Step-Ups - The step-up is a recommended all-around exercise that can be done almost anywhere.
- Not only will it build strength in your quadriceps, but you can also use it as part of a cardio workout.
- It has a low risk of injury.
Overhead Walking Lunges - All that is needed is a weight and room to walk.
- This exercise builds power, strength, and speed in the legs.
- Improves core strength.
Stair Running - This is a high-intensity workout that builds speed, power, and cardiovascular fitness.
- It targets the glutes, quads, and calves.
Agility Drills - Agility drills can include jumping to improve coordination, speed, power, and specific skills.
Sprints - Sprints are quick intense exercises to build muscle and increase performance.
- Sprints use more muscle groups.
Practice - Build strength by performing basic weight training exercises using slow, controlled movements.
- Build power with faster dynamic movements.
- Improve movement speed to create power with explosive, quick exercises.
- Work on form, by incorporating the lead-up to the jump, arm motion, and safe landing technique.
- Include time to practice maximum jumping and bring it all together.
- Always warm up before jumping or performing drills to keep the joints and body safe.
- Athletes jump rope to get the blood circulating and warm up their muscles.
- Do several slow, controlled toe raises to prepare the feet and ankles for jumping and landing.
- Gradually work up to a full vertical jump, by doing box and squat jumps.
Jumping - When finally working on the vertical jump, start with the feet hips-distance apart.
- If measuring jump height, stand about a foot away from the measuring tape or measuring bar on the side.
- Start with arms overhead.
- As you drop into a squat position swing the arms behind the hips.
- Swing back up to the starting position before going for the full jump.
- The pre-swing helps build momentum.
- Land with the knees bent to minimize the impact.
Jumping is a high-impact activity that can take a toll on the knees, hips, ankles, and feet. Be sure to rest the body between hard workouts so the muscles have time to recover, repair, and build up. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Barnes, Jacque L et al. “Relationship of jumping and agility performance in female volleyball athletes.” Journal of Strength and conditioning research vol. 21,4 (2007): 1192-6. doi:10.1519/R-22416.1 Bezerra, Ewertton DE S et al. “Influence of Trunk Position during Three Lunge Exercises on Muscular Activation in Trained Women.” International journal of exercise science vol. 14,1 202-210. 1 Apr. 2021 Hedlund, Sofia, et al. “Effect of chiropractic manipulation on vertical jump height in young female athletes with talocrural joint dysfunction: a single-blind randomized clinical pilot trial.” Journal of Manipulative and physiological therapeutics vol. 37,2 (2014): 116-23. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2013.11.004 Hernández, Sebastian, et al. “Effects of Plyometric Training on Neuromuscular Performance in Youth Basketball Players: A Pilot Study on the Influence of Drill Randomization.” Journal of sports science & medicine vol. 17,3 372-378. 14 Aug. 2018 Karatrantou, Konstantina, et al. “Can sport-specific training affect vertical jumping ability during puberty?.” Biology of sport vol. 36,3 (2019): 217-224. doi:10.5114/biolsport.2019.85455 Markovic, Goran. “Does plyometric training improve vertical jump height? A meta-analytical review.” British Journal of sports medicine vol. 41,6 (2007): 349-55; discussion 355. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2007.035113 McLellan, Christopher P et al. “The role of rate of force development on vertical jump performance.” Journal of Strength and conditioning research vol. 25,2 (2011): 379-85. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181be305c Rodríguez-Rosell, David, et al. “Traditional vs. Sport-Specific Vertical Jump Tests: Reliability, Validity, and Relationship With the Legs Strength and Sprint Performance in Adult and Teen Soccer and Basketball Players.” Journal of Strength and conditioning research vol. 31,1 (2017): 196-206. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000001476 Vanezis, Athanasios, and Adrian Lees. “A biomechanical analysis of good and poor performers of the vertical jump.” Ergonomics vol. 48,11-14 (2005): 1594-603. doi:10.1080/00140130500101262
Regular exercise and physical activity help with cardiovascular health, improved mood, better management of chronic conditions, and can help digestion. For individuals with any GI distress or inflammatory bowel disease that has caused digestive enzyme deficiencies, exercise, and physical movement have been found to provide digestive aid. Here we look at activities to help digestion. Exercises To Help Digestion When exercising the body, the cardiac output/volume of blood the heart pumps every minute increases as the demand for oxygenated blood throughout the body increases, particularly in the working muscles. During exercise, the same increase in blood circulation happens within the digestive system's muscle groups. The blood flow to digestive organs causes peristalsis, which is involuntary constriction and relaxation of the muscles in the digestive tract. This process helps move food efficiently through the gastrointestinal tract. Exercise supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria to maintain a healthy digestive system. - Exercise helps relieves stress which means lower amounts of cortisol.
- Research has found that elevated cortisol levels are associated with compromised digestive function.
- Chronic cortisol production can cause:
- Increased intestinal permeability.
- Impaired absorption of micronutrients.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort.
Types of Exercise - Sticking to moderate-intensity workouts supports a healthy gut microbiome and reduces inflammation.
- Whereas high-intensity exercise sends blood away from the core and toward the extremities to power the muscles, which does not help digestion.
- High-intensity exercise may trigger an inflammatory response, leading to abdominal pain or discomfort, diarrhea, and cramps.
Moderate-intensity exercise activities to try include: Yoga - Yoga is a great stress reduction tool, helping to reduce inflammation that can lead to various gut issues, including constipation and stomach pain.
- Left untreated, chronic inflammation can cause inflammatory bowel disease symptoms to flare.
- Yoga places mild pressure on the digestive organs in certain positions, which can help digestion.
Walking - Walking 30 to 40 minutes three to four times a week can make a digestive difference.
- Walking stimulates blood flow to the intestinal muscles, which helps activate the lymphatic system.
- The gut's lymphatic system helps to absorb and transport lipids and other nutrients throughout the body during digestion.
- The system activates through walking or manual lymphatic massage can improve constipation.
Tai Chi - Tai chi has been shown to improve immune function and inflammation of the gut and is a helpful tool for maintaining homeostasis/gut balance.
- This is a form of moderate-intensity exercise and meditative practice.
- The emphasis is on slow controlled movements and deep breathing.
- This makes it recommended for individuals looking to improve digestion and those with gastrointestinal conditions.
Pilates - Pilates is the practice that targets abdominal muscles and utilizes diaphragmatic breathing to help individuals perform a series of movements to strengthen and elongate the body’s muscles.
- Individuals who perform this exercise often report relief from bloating and gas.
- Exercises like rolling like a ball or the swan dive are great for the digestive organs.
Digestion Goals Whether new to exercise or returning, a plan can help you get there. Meeting with a fitness trainer or sports chiropractor is a great place to begin if you have limited knowledge about what works best for your body and schedule. - A certified trainer can help guide you toward an achievable program that focuses on gut health.
- Individuals with a GI disorder should talk with their doctors before starting a new exercise plan.
- This does not mean you can’t do intense exercises like running; you’ll want to work with a doctor to set up a program that doesn’t cause flare-ups.
- Aim for roughly three hours of moderate-intensity weekly exercise to support a healthy digestive system.
- Sit less and move more.
- Do at least two or more muscle-strengthening activities of moderate intensity every week.
- An anti-inflammatory diet may aid digestion.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Cherpak, Christine E. “Mindful Eating: A Review Of How The Stress-Digestion-Mindfulness Triad May Modulate And Improve Gastrointestinal And Digestive Function.” Integrative medicine (Encinitas, Calif.) vol. 18,4 (2019): 48-53. Drouin, Jacqueline S et al. “Comparisons between Manual Lymph Drainage, Abdominal Massage, and Electrical Stimulation on Functional Constipation Outcomes: A Randomized, Controlled Trial.” International Journal of environmental research and public health vol. 17,11 3924. June 1. 2020, doi:10.3390/ijerph17113924 Hamasaki, Hidetaka. “Exercise and gut microbiota: clinical implications for the feasibility of Tai Chi.” Journal of integrative medicine vol. 15,4 (2017): 270-281. doi:10.1016/S2095-4964(17)60342-X Joyner, Michael J, and Darren P Casey. “Regulation of increased blood flow (hyperemia) to muscles during exercise: a hierarchy of competing physiological needs.” Physiological Reviews vol. 95,2 (2015): 549-601. doi:10.1152/physrev.00035.2013 LeBouef T, Yaker Z, Whited L. Physiology, Autonomic Nervous System. [Updated 2023 May 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538516/ Singhal, Rashi, and Yatrik M Shah. “Oxygen battle in the gut: Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic and inflammatory responses in the intestine.” The Journal of biological chemistry vol. 295,30 (2020): 10493-10505. doi:10.1074/jbc.REV120.011188 van Wijck, Kim, et al. “Physiology and pathophysiology of splanchnic hypoperfusion and intestinal injury during exercise: strategies for evaluation and prevention.” American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology vol. 303,2 (2012): G155-68. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00066.2012
Introduction Everyone, at some point, has some form of physical activity that helps them release the stresses of everyday factors. Whether for athletic training or to keep a healthy lifestyle, exercising for at least 30 minutes to an hour can help promote muscle growth and toning, reducing stress and high blood pressure. However, many individuals would often not be able to find time to exercise, which can lead to many problems in their bodies. When many individuals are physically inactive, it can lead to musculoskeletal pain, weak muscles, and other chronic conditions. To that point, it can make the person miserable and cause disability. Luckily numerous therapies can help reduce the effects of pain-like symptoms associated with physical inactivity and can help restore the body. Today’s article focuses on how MET (muscle energy techniques) therapy uses a chair and abdominal exercises to help promote spinal flexibility, reduce abdominal weakness, and strengthen low back and pelvic muscles. We utilize and incorporate valuable information about our patients to certified medical providers using the chair and abdominal exercises in MET therapy. We encourage and refer patients to associated medical providers based on their findings while supporting that education is a remarkable and fantastic way to ask our providers the essential questions at the patient’s acknowledgment. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., comprises this information as an educational service. Disclaimer Chair Exercises In MET Therapy Are you experiencing muscle pain in specific areas of your body? Do your legs feel tired after a long day at work or when you bend down to pick something up? These musculoskeletal pain symptoms are often caused by physical inactivity, which can cause muscles to become weak and short. This can lead to various health issues related to musculoskeletal pain if not addressed. However, you can help reduce these effects by incorporating everyday objects like a chair into your exercise routine. Research studies have revealed that chair-based exercises can provide cognitive and psychological benefits while reducing the risk of injury. Additionally, using a chair for exercise can improve spinal flexibility. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
The biceps curl is an exercise to build strength in the upper arm. Curls are a common exercise used in upper-body strength training. Specifically, the curl works the muscles in the front of the upper arm. It's recommended for achieving strength and definition and provides core and stability challenges. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can educate individuals on fitness, strength training, nutrition, and injury prevention. Bicep Curls Located at the upper arm, the biceps comprise a short and long head that operates as a single muscle. - The bicep heads begin at different places around the shoulder/scapula region,
- They have a common insertion point on the elbow tendon.
- Together allow the bending of the arm at the elbow joint to curl and pull weight.
- Curls work the muscles at the front of the upper arm and the lower arm. The brachialis and brachioradialis.
Dumbbells Different equipment and grips can be used, including dumbbell weights, kettlebells, barbells, resistance bands, or cable machines. Select equipment with enough weight that can be lifted ten times using proper form, ensuring the last three repetitions are challenging to the point of being unable to raise another. From there, use this same weight to perform eight repetitions or slightly lower the weight and perform ten repetitions. - Begin by standing with the feet about hip-width apart.
- Keep the abdominal/core muscles engaged.
- Hold one dumbbell in each hand.
- Relax the arms down at the sides with palms facing forward.
- Keep the upper arms stable and shoulders relaxed.
- Bend at the elbow and lift the weights so the dumbbells approach the shoulders.
- Raise the dumbbells to eye or forehead level for a full range of motion.
- Tension will be felt in the muscles in the front of the upper arm.
- Keep movements smooth and controlled.
- The elbows should stay tucked in close to the body.
- Be careful to keep the wrist straight and rigid.
- Flexing the wrist while bending the elbow won't target the biceps effectively and can result in a wrist or elbow injury.
- Exhale while lifting.
- Lower the weights to the starting position.
- For most, one set of 12 to 15 repetitions is adequate.
- Train to failure performing the desired reps, staying within 3 to 5 repetitions of total failure.
- When able, slightly increase weight and/or reps over time to increase muscle and strength.
- Both biceps can be worked out by alternating arms.
- It can be done standing or sitting.
Avoid Errors Get the most out of the workout by avoiding these errors. Rushing Through - Focus on proper form and avoid rushing through the workout.
- Lift the weights with a smooth motion.
- Take as much time to lower the weight as when lifting it.
- Lowering the weight slowly can help build more muscle, making the most of the workout.
Improper Elbow Position - The position of the elbows should remain close to the side of the body.
- Only the lower arm should move until the end of the movement when the elbows rise. This is a complete range of motion.
- If the elbows move away from the torso or swing behind the body, there is probably too much weight.
Avoid Swinging the Weights - Focus on maintaining a tall, upright spine and a tight core.
- The shoulders or torso should not swing the weights up when doing the curl.
- It can feel like swinging, twisting, or heaving movements.
- Don't let the hips hinge, or the lower body assist the movement.
- Keep the elbows at the sides until they naturally rise at the end of the motion.
- Keep the shoulders relaxed
- Make sure the shoulders don't move forward to initiate the movement.
- Use lighter weights or reduce the number of repetitions if this happens.
Safety This exercise is generally recommended for most individuals. However, getting clearance from a primary caregiver before beginning any exercise routine is recommended. - Individuals with an arm injury or who experience pain during the motion should not perform the exercise without a doctor's approval.
- Don't try to lift weights that are too heavy.
- After a few lifts, expect to feel fatigued and a burning sensation in the biceps and forearm muscles.
- This is the desired effect to get the muscles strong and growing.
- Do not force extra repetitions once proper form cannot be achieved.
- Take a thorough rest before the next set.
- Stop if pain begins to present.
Benefits - These muscles are in constant use when picking things up.
- Consistently performing the biceps curl will help build strength in the upper arm.
- Individuals learn to use their arm muscles correctly and with the core muscles.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Coratella, Giuseppe, et al. “Biceps Brachii and Brachioradialis Excitation in Biceps Curl Exercise: Different Handgrips, Different Synergy.” Sports (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,3 64. 9 Mar. 2023, doi:10.3390/sports11030064 Coratella, Giuseppe, et al. “Bilateral Biceps Curl Shows Distinct Biceps Brachii and Anterior Deltoid Excitation Comparing Straight vs. EZ Barbell Coupled with Arms Flexion/No-Flexion.” Journal of functional morphology and Kinesiology vol. 8,1 13. 19 Jan. 2023, doi:10.3390/jfmk8010013 Marchetti, Paulo H et al. “Seated row and biceps curl exercises present similar acute responses on muscle thickness, arm circumference, and peak force for elbow flexors after a resistance training session in recreationally-trained subjects.” The Journal of sports medicine and physical fitness vol. 60,11 (2020): 1415-1422. doi:10.23736/S0022-4707.20.10996-4 Sato, Shigeru, et al. “Elbow Joint Angles in Elbow Flexor Unilateral Resistance Exercise Training Determine Its Effects on Muscle Strength and Thickness of Trained and Non-trained Arms.” Frontiers in physiology vol. 12 734509. 16 Sep. 2021, doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.734509 Schoenfeld, Brad Jon, et al. “Differential effects of attentional focus strategies during long-term resistance training.” European Journal of sports science vol. 18,5 (2018): 705-712. doi:10.1080/17461391.2018.1447020
Introduction An exercise routine is highly important for anyone trying to get a kick start on their health and wellness journey. It could be simple as walking around the park for 30 minutes, going to the community pool to swim, or taking a group fitness class with friends. Incorporating an exercise regime can even help reduce the effects of musculoskeletal disorders and their associated symptoms from causing pain in the muscles and joints in the body. Even though many individuals have busy lives, it is important to ensure that their bodies are getting enough exercise to feel less joint and muscle pain while improving other systems that benefit from training. Today’s article looks at how to keep a constant exercise routine, how exercise can help musculoskeletal disorders, and how the MET technique is combined with physical activity. We provide and mention valuable information about our patients to certified medical providers who offer available therapy treatments like the MET technique combined with physical activities for individuals dealing with musculoskeletal pain disorders. We encourage each patient by referring them to our associated medical providers based on the patient’s diagnosis findings appropriately. We acknowledge that education is a spectacular way when asking our providers the most helpful questions at the patient’s acknowledgment. Dr. Alex Jimenez, D.C., utilizes this information as an educational service. Disclaimer Keeping A Constant Exercise Routine Have you been feeling sluggish throughout the day? Do you believe you don’t have enough time to exercise and feel stressed? Or have you been experiencing unwanted pain and stiffness in your muscles and joints? Many individuals experiencing these issues in their bodies could not be getting enough exercise to reduce these musculoskeletal disorders. When it comes to many individuals trying to keep a constant exercise routine to better their health may be difficult but not impossible. There are many ways to incorporate a daily consistent exercise routine by making small changes in your daily life routine. Walking with friends or pets, attending a group fitness class, or doing squats at home can benefit muscle growth and promote motivation to continue these small changes. However, some of the reasons that many people need to exercise more are to need more time. Studies reveal that most people often refrain from any form of exercise due to needing more time out of their busy schedules. People who do not exercise regularly are potentially at risk of developing health-related problems and disorders linked to the musculoskeletal system. Exercise For Musculoskeletal Disorders When the musculoskeletal system is linked to health-related problems due to physical inactivity, when the body is not getting enough exercise, it can cause muscle and joint pain and other associated symptoms that can affect mobility. Research studies have revealed that pain in specific areas of the body, which includes the back, neck, and shoulders, is often due to extended periods of sitting down and inactivity that cause many people to develop musculoskeletal disorders. When pain and discomfort affect the body, it can cause visceral-somatic pain in different body areas. Not only that, but the various muscles in the upper and lower extremities of the body will become shortened and weak over time, leading to disability and poor posture. Now all is not lost, as there are ways to reduce the effects of musculoskeletal disorders and incorporate exercise as part of a person’s daily routine. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
|
Can incorporating various yoga poses help reduce neck tension and provide pain relief for individuals dealing with neck pain? Introduction Within the hustling and bustling of modern life, it is common for many individuals to carry stress in their bodies. When the body deals with everyday stressors, tension, discomfort, and pain can often manifest in the upper and lower portions of the body. When the body’s upper and lower portions deal with these issues, they can cause overlapping risk profiles in the musculoskeletal system. One of the most common musculoskeletal issues is neck pain. It can cause many problems to the cervical portion of the spine and cause the surrounding muscles to become tense and in pain from the stress of everyday responsibilities. Luckily, there are numerous ways to reduce stress from the neck and help relax the affected muscles from discomfort, including yoga. In today’s article, we will look at how neck pain affects the upper body, the benefits of yoga for neck pain, and various yoga poses to reduce the overlapping effects of neck pain. We discuss with certified medical providers who consolidate our patients’ information to assess how neck pain is correlated with everyday stressors that affect the upper body. We also inform and guide patients on how yoga and the various poses can benefit the body and provide pain relief to the surrounding muscles. We also encourage our patients to ask their associated medical providers many intricate and important questions about incorporating yoga into their daily routine to reduce muscle tension and provide clarity to their bodies. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer. How Does Neck Pain Affect The Upper Body? Do you feel discomfort or pain in your neck and shoulders after a long, hard workday? Do you notice you hunched more than usual when doing your daily routine? Or do you see yourself developing a hunched posture from looking at the computer screen or phone for an extended period? Many of these normal motions are often correlated with the upper body, especially in the neck and shoulder regions, which causes neck pain. As one of the most common problems affecting many people worldwide, neck pain is a multifactorial disease with numerous risk factors contributing to its development. (Kazeminasab et al., 2022) Like back pain, neck pain can have acute and chronic stages depending on the severity and environmental factors leading to its development. The various muscles, ligaments, and tissues surrounding the neck and shoulders keep the neck stable and mobile. When many individuals overuse these muscles in the neck and shoulders repetitively, it can increase neck pain in the upper body in adulthood. (Ben Ayed et al., 2019) When acute neck pain turns chronic, it can cause the individual to be in constant discomfort, pain, and misery, so they start to look for various solutions to reduce the correlating symptoms when speaking to their primary doctors. When many individuals begin to explain to their doctors what their daily routine looks like, many doctors will start to assess and formulate a plan that focuses on any specific description of any injuries, including potential mechanisms, inciting and relieving factors, and pain patterns they have encountered throughout the day to come up with a personalized treatment plan to not only reduce neck pain but also provide relief to tension and discomfort to the body. (Childress & Stuek, 2020) General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Can incorporating acupressure provide effective relief and benefits for individuals looking to try natural treatments for common health ailments? Acupressure Acupressure is a type of complementary medicine that is rising in popularity due to its simplicity and accessibility. It can assist in treating various diseases and conditions. (Piyush Mehta et al., 2016) Anyone can learn it, and no special equipment is required. It is an effective and safe therapeutic option with no known side effects. (Youngmi Cho et al., 2021) It is a cost-effective intervention similar to acupuncture. (Lukas Israel et al., 2021) What Is It? The concept of acupressure activates acupoints or pressure points across meridians or channels connected to various organs to balance energy and promote health. Practitioners believe that the quality or state of a person's energy determines their health. (Piyush Mehta et al., 2016) Acupressure is the stimulation of acupoints using either the fingers or a tool. Massage techniques like Amma, Shiatsu, Tui Na, and Thai massage incorporate acupressure in their treatments and follow the same energy channels as acupuncture. The Way It Works Acupressure works similarly to acupuncture. The Gate Control Theory theorizes that pleasure impulses reach the brain four times faster than pain impulses. Continuous pleasurable impulses close the neural gates and block slower messages, like pain. According to this theory, acupressure improves the pain perception threshold. (Piyush Mehta et al., 2016) Stimulating acupoints activates functional responses, like releasing hormones. These hormones serve various functions, physical, like regulating organ function, and mental, like regulating emotions, and releasing them can help improve health and well-being. (Piyush Mehta et al., 2016) - Acupressure is a simple and effective intervention that can be self or professionally administered.
- Acupoints are activated in the elbows, fingers, feet, knuckles, palms, or thumbs.
- Though acupressure doesn’t require specialized tools, they are available for convenience.
- Some practitioners used Bian stones to activate acupoints.
- Modern tools can assist with activating acupoints. (Piyush Mehta et al., 2016)
- Pressing the acupoints is adequate, and inaccuracies are unlikely to cause harm or injury. (Youngmi Cho et al., 2021)
Some of the tools available include: (Piyush Mehta et al., 2016) - Spinal device
- Gloves
- Device for fingers
- Pen
- Ring
- Footwear
- Footboard
- Device for ear
- Clamps
Benefits Acupressure is often used alongside modern medicine, as it treats common or coexisting symptoms, such as anxiety or stress. Some of the conditions for which acupressure may be effective include. Stress and Fatigue Reduction Stress and fatigue are common but often arise alongside other ailments or conditions if persistent or severe, anxiety and fatigue can significantly affect quality of life by reducing an individual's ability to participate in daily activities. In a study looking at shift work nurses who experience stress and fatigue from the intensity of their work, acupressure significantly reduced their symptoms. (Youngmi Cho et al., 2021) In studies with breast cancer survivors, acupressure was also used to decrease fatigue levels and was shown to be an effective and low-cost option for managing persistent fatigue alongside standard care for breast cancer. (Suzanna Maria Zick et al., 2018) (Suzanna M Zick et al., 2016) Can Help With Anxiety and Depression Depression and anxiety can be part of a disorder or exist on their own. Acupressure may help alleviate some of the anxiety and depression that arise as part of a condition or ailment. In the shift work nurses study, acupressure helped decrease anxiety levels. (Youngmi Cho et al., 2021) In other studies, acupressure reduced anxiety scores and improved depressive symptoms in individuals with mild to moderate symptoms. (Elizabeth Monson et al., 2019) (Jingxia Lin et al., 2022) (Suzanna Maria Zick et al., 2018) Pain Reduction Individuals experience physical pain for a variety of reasons. Pain can come from temporary sports injuries, work, sudden awkward movements, and/or chronic illness. Acupressure can effectively reduce pain as a complementary therapy. (Elizabeth Monson et al., 2019) In a study, athletes who had a musculoskeletal sports injury reported decreased pain intensity after three minutes of acupressure therapy. (Aleksandra K Mącznik et al., 2017) In another study, breast cancer survivors showed significant improvements with acupressure. (Suzanna Maria Zick et al., 2018) Nausea Relief Nausea and vomiting are conditions that are common for those who are pregnant or undergoing chemotherapy. It also can be a medication side effect or arise with migraine or indigestion. There is evidence that acupressure may be effective in alleviating symptoms. Some researchers believe a particular type of acupressure known as auricular acupressure is the most effective for treating chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting alongside standard treatment. (Jing-Yu Tan et al., 2022) However, further research is needed to determine whether this is a viable, ongoing option for treating nausea and vomiting. (Heather Greenlee et al., 2017) Sleep Better Acupressure can be an effective and low-cost option for managing breast cancer symptoms. One study found relaxing acupressure techniques improved sleep quality and quality of life in breast cancer survivors. Additionally, researchers note that relaxing acupressure is more effective for improving sleep and quality of life than stimulating acupressure. (Suzanna M Zick et al., 2016) Allergy Reduction Allergic rhinitis is inflammation caused by an allergic reaction. Previous trials have found that acupressure could improve overall health by reducing seasonal allergic rhinitis symptoms and the need for allergy medication. (Lukas Israel et al., 2021) Researchers also noted that individuals are likely to adhere to self-applied acupressure therapy as a form of self-massage. (Lukas Israel et al., 2021) Always consult a healthcare provider before starting acupressure treatments, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions. At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we treat injuries and chronic pain syndromes by developing personalized treatment plans and specialized clinical services focused on injuries and the complete recovery process. Flexibility, mobility, and agility programs are tailored for all age groups and disabilities. If other treatment is needed, individuals will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited to their injury, condition, and/or ailment. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Mehta, P., Dhapte, V., Kadam, S., & Dhapte, V. (2016). Contemporary acupressure therapy: Adroit cure for painless recovery of therapeutic ailments. Journal of traditional and complementary medicine, 7(2), 251–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.06.004 Cho, Y., Joo, J. M., Kim, S., & Sok, S. (2021). Effects of Meridian Acupressure on Stress, Fatigue, Anxiety, and Self-Efficacy of Shiftwork Nurses in South Korea. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(8), 4199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084199 Israel, L., Rotter, G., Förster-Ruhrmann, U., Hummelsberger, J., Nögel, R., Michalsen, A., Tissen-Diabaté, T., Binting, S., Reinhold, T., Ortiz, M., & Brinkhaus, B. (2021). Acupressure in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled exploratory trial. Chinese medicine, 16(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-021-00536-w Zick, S. M., Sen, A., Hassett, A. L., Schrepf, A., Wyatt, G. K., Murphy, S. L., Arnedt, J. T., & Harris, R. E. (2018). Impact of Self-Acupressure on Co-Occurring Symptoms in Cancer Survivors. JNCI cancer spectrum, 2(4), pky064. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncics/pky064 Zick, S. M., Sen, A., Wyatt, G. K., Murphy, S. L., Arnedt, J. T., & Harris, R. E. (2016). Investigation of 2 Types of Self-administered Acupressure for Persistent Cancer-Related Fatigue in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA oncology, 2(11), 1470–1476. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.1867 Monson, E., Arney, D., Benham, B., Bird, R., Elias, E., Linden, K., McCord, K., Miller, C., Miller, T., Ritter, L., & Waggy, D. (2019). Beyond Pills: Acupressure Impact on Self-Rated Pain and Anxiety Scores. Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.), 25(5), 517–521. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2018.0422 Lin, J., Chen, T., He, J., Chung, R. C., Ma, H., & Tsang, H. (2022). Impacts of acupressure treatment on depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World journal of psychiatry, 12(1), 169–186. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.169 Mącznik, A. K., Schneiders, A. G., Athens, J., & Sullivan, S. J. (2017). Does Acupressure Hit the Mark? A Three-Arm Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Acupressure for Pain and Anxiety Relief in Athletes With Acute Musculoskeletal Sports Injuries. Clinical journal of sport medicine : official journal of the Canadian Academy of Sport Medicine, 27(4), 338–343. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0000000000000378 Tan, J. Y., Molassiotis, A., Suen, L. K. P., Liu, J., Wang, T., & Huang, H. R. (2022). Effects of auricular acupressure on chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in breast cancer patients: a preliminary randomized controlled trial. BMC complementary medicine and therapies, 22(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-022-03543-y Greenlee, H., DuPont-Reyes, M. J., Balneaves, L. G., Carlson, L. E., Cohen, M. R., Deng, G., Johnson, J. A., Mumber, M., Seely, D., Zick, S. M., Boyce, L. M., & Tripathy, D. (2017). Clinical practice guidelines on the evidence-based use of integrative therapies during and after breast cancer treatment. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 67(3), 194–232. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21397 Ho, K. K., Kwok, A. W., Chau, W. W., Xia, S. M., Wang, Y. L., & Cheng, J. C. (2021). A randomized controlled trial on the effect of focal thermal therapy at acupressure points treating osteoarthritis of the knee. Journal of orthopaedic surgery and research, 16(1), 282. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02398-2
"Can understanding moderate exercise and how to measure the amount of exercise help expedite individuals' health goals and well-being?" Moderate Exercise Various physical activity guidelines recommend regular, moderate exercise for achieving and maintaining health and wellness. Getting the minimum, moderate weekly physical activity can help prevent disease, increase mental well-being, support weight loss and maintenance, and improve quality of life. What Is It? - Anything that gets the heart pumping and beating faster is considered moderate exercise. (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2018)
- Moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise includes - brisk walking, yard work, mopping, vacuuming, and playing various sports that require consistent movement.
- When engaged in moderate exercise, individuals should breathe harder but still be able to carry a conversation. (American Heart Association, 2024)
- The talk test is a way to monitor whether the exercise is at moderate intensity.
Benefits Regular moderate exercise can help (American Heart Association, 2024) - Decrease the risk of developing conditions like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and dementia.
- Improve sleep and help with sleep disorders.
- Improve brain functions like memory, focus, and processing.
- With weight loss and/or maintenance.
- Improve bone health.
- Reduce depression, anxiety, and other mental health symptoms.
How Much Exercise? The prescription for moderate exercise includes: - 30 minutes a day for five days a week, or two hours and 30 minutes per week. (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2018)
- Physical activity needs to continue for at least 10 minutes to be considered an exercise session.
- Individuals can break up their 30 daily minutes into two to three shorter sessions, each 10 minutes long.
- As the ability to exercise increases, aim to increase moderate activities.
- Individuals will reap even more health benefits if they increase moderate aerobic exercise time to 300 minutes or five hours weekly. (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2018)
Measuring Exercise - A moderate level of activity noticeably increases heart and breathing rate.
- Individuals sweat but can still carry on a conversation.
- Individuals can talk but can't sing.
- Individuals will feel the exercise but are not huffing and puffing.
- Individuals can use different scales to measure exercise intensity.
Heart Rate - A moderate-intensity heart rate is 50% to 70% of an individual's maximum heart rate. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022)
- An individual's maximum heart rate varies by age.
- A heart rate chart or calculator can determine an individual's maximum heart rate.
- To measure heart rate mid-exercise, individuals can take their pulse or use a heart rate monitor, app, fitness tracker, or smartwatch to ensure they stay at a moderate intensity.
MET - M.E.T. stands for Metabolic Equivalent for Task and refers to the amount of oxygen the body uses during physical activity.
- Assigning METs to an activity allows individuals to compare the amount of exertion an activity takes.
- This works for individuals with different weights.
- During moderate physical activity, breathing and heart rate increase, and the body burns around 3.5 to 7 calories a minute.
- The actual number burned depends on your weight and fitness level.
- The body uses 1 MET for basic functions like breathing.
- Grades of activity:
- 1 MET - Body at rest
- 2 METs - Light activity
- 3-6 METs - Moderate activity
- 7 or more METs - Vigorous activity
Perceived Exertion Scale Individuals can also check their activity level using the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion scale/RPE. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022) Using this scale involves monitoring how an individual feels about how hard their body is working during physical activity. The scale starts at 6 and ends at 20. A perceived exertion between 11 and 14 is considered moderate physical activity. - 6 - No exertion - sitting still or sleeping
- 7-8 - Extremely light exertion
- 9-10 - Very light exertion
- 11-12 - Light exertion
- 13-14 - Somewhat hard exertion
- 15-16 - Heavy exertion
- 17-18 - Very heavy exertion
- 20 - Maximum exertion
Examples Many activities are counted as moderate-intensity exercise. Choose some appealing and learn to add them to a weekly routine. - Ballroom dancing
- Line dancing
- Gardening
- House chores that get the heart pumping.
- Softball
- Baseball
- Volleyball
- Doubles tennis
- Brisk walking
- Light jogging
- Walking or jogging on a treadmill
- Using an elliptical trainer
- Bicycling under 10 miles an hour on ground level
- Leisurely swim
- Water aerobics
Mobility Challenges - Individuals with mobility issues can achieve moderate intensity using a manual wheelchair or a handcycle and swimming or water aerobics.
- Individuals who can use their legs but can't tolerate walking or jogging can try bicycling or swimming.
Getting More Exercise There are different ways to incorporate and increase moderate physical activities. These include: 10-minute Activity Bursts - Walk briskly for at least 10 minutes at a time.
- Walk at an easy pace for a couple of minutes.
- Pick up the pace for 10 minutes.
- Try to walk during work breaks or lunch and/or before or after work.
Walking Workouts - Individuals can walk indoors, outdoors, or on a treadmill.
- Proper posture and walking techniques make it easier to achieve a brisk pace.
- Once comfortable walking briskly for 10 minutes, begin to extend walking time.
- Try different walking workouts that offer fast walks, jogging intervals, and/or adding hills or treadmill inclines.
New Activities - Individuals are recommended to experiment with various exercises to find what works for them.
- Consider roller skating, blading, or skateboarding to increase heart rate.
Moderate physical activity will get and keep the body in shape. Individuals should not become distressed if they can only do a little at first. Allow time to build endurance and gradually make time each day for enjoyable physical activities. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. (2018). Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd edition. Retrieved from https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf American Heart Association. (2024). American Heart Association recommendations for physical activity in adults and kids. (Healthy Living, Issue. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/fitness/fitness-basics/aha-recs-for-physical-activity-in-adults Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Target heart rate and estimated maximum heart rate. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/measuring/heartrate.htm Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Perceived exertion (Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/measuring/exertion.htm
For individuals who have decided to start exercising for fitness and health, walking is a great place to start. Can planning a walking exercise schedule help individuals maintain a fitness routine and improve endurance and speed quicker? Walking Exercise Planning Schedule While any amount of walking benefits health, individuals can increase the benefits by walking more per week or by increasing the pace. Brisk walking for 30 minutes per day, totaling 150 minutes per week, is recommended by health experts to decrease risks for heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and other conditions. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022) - Individuals with ongoing health conditions should talk to their doctor before starting any new exercise program.
- Beginners are encouraged to focus on using proper walking posture and technique to steadily improve strength and endurance.
- The increased duration or intensity can help if weight loss is a goal.
- Improving diet is also necessary for the best results.
- Individuals can build healthy walking habits by tracking walks.
Schedule Checklist - Individuals can walk outdoors, indoors, or on a treadmill.
- Wear proper athletic shoes and clothing.
- Check walking posture.
- Walk at an easy pace for a couple of minutes before picking up speed.
First Week An example of what a walking exercise schedule can look like, but it's advised to consult a professional trainer to develop a personalized fitness plan. - Start with a 15-minute walk at an easy pace.
- Walk five days the first week.
- Building a healthy habit is the goal, so consistency is important.
- Spread out rest days, like making days 3 and 6 rest days.
- Weekly goal - 60 to 75 minutes
Second Week - Add five minutes, so the walk time increases gradually.
Or, individuals can extend more on some days, followed by a rest day. - Weekly goal - 80 to 100 minutes
Third Week - Add five more minutes with each session, so the walk increases to 25 minutes.
- Weekly goal - 100 to 125 minutes
Fourth Week - Add another five minutes to increase the walk to 30 minutes.
- Weekly goal - 120 to 150 minutes
Individuals who find any week to be difficult are suggested to repeat that week instead of adding time until they are able to progress naturally. Once able to walk for 30 minutes at a time comfortably, individuals are ready for a variety of different walking exercise workouts to add intensity and endurance. A weekly walking plan can include: - Longer walks
- Higher-intensity walks
- Speed-building walks
Beginner Walking Speed An individual's objective should be brisk walking to achieve a moderate-intensity workout. This is the intensity that is associated with the most health benefits. Brisk walking should feel like: - Breathing is heavier than normal.
- Able to carry a full conversation while walking.
- Not out of breath. (Siti Ruzita Mahmod et al., 2018)
- If the speed is slower and the heart rate is lower during the initial weeks, this is normal.
- The first goal is to walk for 30 to 60 minutes a day without injury.
- Adding speed and intensity gradually.
- Staying consistent in regularly walking before trying to walk faster and longer.
- Using proper walking posture and arm motion will help in faster walking.
- To reduce the risk of injury, gradually increase the length of the walk or pace, only changing one component at a time.
Individuals may consider joining a walking group or club to have others to walk with and an incentive to maintain regular walking. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). How Much Physical Activity Do Adults Need? Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/adults/index.htm Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Measuring Physical Activity Intensity. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/measuring/index.html Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Target Heart Rate and Estimated Maximum Heart Rate. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/measuring/heartrate.htm Mahmod, S. R., Narayanan, L. T., & Supriyanto, E. (2018). Effects of incremental cardiorespiratory exercise on the speech rate and the estimated exercise intensity using the counting talk test. Journal of physical therapy science, 30(7), 933–937. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.30.933
For individuals working at a desk or work station where the majority of the work is done in a sitting position and increases the risk for a variety of health problems, can using a standing desk help prevent musculoskeletal problems and improve short and long-term wellness? Stand Desks More than 80% of jobs are done in a seated position. Stand desks have proven to help. (Allene L. Gremaud et al., 2018) An adjustable stand desk is intended to be the standing height of an individual. Some desks can be lowered to use while sitting. These desks can improve: - Blood circulation
- Back pain
- Energy
- Focus
- Individuals who are less sedentary may experience decreased depression, anxiety, and risk of chronic disease.
Improve Posture and Decrease Back Pain Sitting for prolonged periods can cause fatigue and physical discomfort. Back pain symptoms and sensations are common, especially when practicing unhealthy postures, already dealing with existing back problems, or using a non-ergonomic desk set-up. Instead of only sitting or standing for the whole workday, alternating between sitting and standing is far healthier. Practicing sitting and standing regularly reduces body fatigue and lower back discomfort. (Alicia A. Thorp et al., 2014) (Grant T. Ognibene et al., 2016) Increases Energy Levels Prolonged sitting correlates with fatigue, reduced energy, and productivity. A sit-stand desk can provide benefits like increased productivity levels. Researchers discovered that sit-stand desks could improve the general health and productivity of office workers. Individuals in the study reported: - A significant increase in subjective health.
- Increased energy in work tasks.
- Improved work performance. (Jiameng Ma et al., 2021)
Chronic Disease Reduction According to the CDC, six in 10 individuals in the U.S. have at least one chronic disease, like diabetes, heart disease, stroke, or cancer. Chronic disease is the leading cause of death and disability, as well as a leading force of healthcare costs. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023) While further research is needed to see if standing desks can reduce the risk of chronic disease, one study looked to quantify the association between sedentary time and the risk of chronic disease or death. Researchers reported that sedentariness for prolonged periods was independently associated with negative health outcomes regardless of physical activity. (Aviroop Biswas et al., 2015) Improved Mental Focus Sitting for extended periods slows down blood circulation. This decreased blood flow to the brain lowers cognitive function and increases the risk of neurodegenerative conditions. One study confirmed that healthy individuals who worked in a prolonged sitting position had reduced brain blood flow. The study found that frequent, short walks could help prevent this. (Sophie E. Carter et al., 2018) Standing increases blood and oxygen circulation. This improves cognitive function, which also helps improve focus and concentration. Depression and Anxiety Reduction Modern lifestyles typically contain large amounts of sedentary behavior. However, there is a small amount about the mental health risks of prolonged sedentary behavior. There have been a few studies aimed at improving public understanding. One study focused on a group of older adults, having them self-report sedentary habits that included television, internet, and reading time. This information was compared to their scoring on the Centre of Epidemiological Studies Depression scale. (Mark Hamer, Emmanuel Stamatakis. 2014) - The researchers found that certain sedentary behaviors are more harmful to mental health than others.
- Television watching, for example, resulted in increased depressive symptoms and decreased cognitive function. (Mark Hamer, Emmanuel Stamatakis. 2014)
- Internet use had the opposite effect, decreasing depressive symptoms and increasing cognitive function.
- Researchers theorize that the results come from the contrasting environmental and social contexts in which they are happening. (Mark Hamer, Emmanuel Stamatakis. 2014)
- Another study looked at the possible correlation between sedentary behavior and anxiety.
- Increased amounts of sedentary behavior, especially sitting, seemed to increase the risk of anxiety. (Megan Teychenne, Sarah A Costigan, Kate Parker. 2015)
Incorporating a standing desk into the workspace can help to reduce the negative effects of sedentary behaviors, leading to improved productivity, improved mental and physical health, and a healthy work environment for individuals who work long hours at a desk or workstation. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Gremaud, A. L., Carr, L. J., Simmering, J. E., Evans, N. J., Cremer, J. F., Segre, A. M., Polgreen, L. A., & Polgreen, P. M. (2018). Gamifying Accelerometer Use Increases Physical Activity Levels of Sedentary Office Workers. Journal of the American Heart Association, 7(13), e007735. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.007735 Thorp, A. A., Kingwell, B. A., Owen, N., & Dunstan, D. W. (2014). Breaking up workplace sitting time with intermittent standing bouts improves fatigue and musculoskeletal discomfort in overweight/obese office workers. Occupational and environmental medicine, 71(11), 765–771. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2014-102348 Ognibene, G. T., Torres, W., von Eyben, R., & Horst, K. C. (2016). Impact of a Sit-Stand Workstation on Chronic Low Back Pain: Results of a Randomized Trial. Journal of occupational and environmental medicine, 58(3), 287–293. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0000000000000615 Ma, J., Ma, D., Li, Z., & Kim, H. (2021). Effects of a Workplace Sit-Stand Desk Intervention on Health and Productivity. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(21), 11604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111604 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic disease. Biswas, A., Oh, P. I., Faulkner, G. E., Bajaj, R. R., Silver, M. A., Mitchell, M. S., & Alter, D. A. (2015). Sedentary time and its association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of internal medicine, 162(2), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.7326/M14-1651 Carter, S. E., Draijer, R., Holder, S. M., Brown, L., Thijssen, D. H. J., & Hopkins, N. D. (2018). Regular walking breaks prevent the decline in cerebral blood flow associated with prolonged sitting. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 125(3), 790–798. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00310.2018 Hamer, M., & Stamatakis, E. (2014). Prospective study of sedentary behavior, risk of depression, and cognitive impairment. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 46(4), 718–723. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000156 Teychenne, M., Costigan, S. A., & Parker, K. (2015). The association between sedentary behaviour and risk of anxiety: a systematic review. BMC public health, 15, 513. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1843-x
Individuals dealing with chronic knee discomfort, hip tightness, and lower back pain could be experiencing dormant gluteal-butt syndrome. Can recognizing the symptoms and signs and incorporating lower body and core fitness help prevent and treat the condition? Dormant Gluteal Butt Syndrome Knee, hip, and lower back problems could be traced back to weakened buttocks. Some scientists call the condition "dormant butt syndrome" (Ohio State University, .2023). However, researchers are learning about the important role the gluteal muscles provide in maintaining the lower body strong and healthy. (Hal David Martin, Manoj Reddy, Juan Gómez-Hoyos. 2015) What Is It? The syndrome is defined as weak buttock muscles and tight hip flexors. Experts from the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center have worked with individuals dealing with knee, hip, or back injuries and believe many of these issues are linked to weakened gluteal muscles. (Ohio State University.2023) The glutes are the muscles of the hips and buttocks. Weakened muscles fail to absorb the shock they're supposed to during activities, which results in overloading the surrounding muscles and joints and increases the risk of injury. (Ohio State University, .2023) - Dormant gluteal-butt syndrome can result from a sedentary lifestyle and prolonged inactivity, like sitting for long periods.
- The condition also occurs in runners and other physically active individuals who forget about these muscles with targeted exercises.
Exercises Exercises to target the gluteals and prevent dormant gluteal-butt syndrome include activities/exercises that work the hips and core. - When walking properly, the gluteals should execute hip extension naturally.
- Unhealthy postures, excessive sitting, and continued dysfunctional biomechanics mean walking without achieving optimal hip extension. (Hadi Daneshmandi. 2017)
- When this happens, the gluteal muscles never get to fully function work, ending up with a series of aches and pains.
- Pilates exercises can be adjusted to address order, repetition, and variation to strengthen the gluteals. (Laís Campos de Oliveira, 2015)
Hamstring Curls - Lie face down on an exercise mat.
- Use your hands to create a cushion for the forehead.
- Bend both knees so the feet point up towards the ceiling.
- Let the knees be slightly apart, but keep the heels together.
- Squeeze the heels together and tighten the gluteal muscles.
- Hold for 3 seconds, then release the buttocks.
- Repeat 10 times and then rest.
- Hamstring curls can also be done using a weight machine.
Leg Pull Ups - Sit on a mat with your legs together in front.
- Place the hands just behind the backside with the fingers pointing forward if possible.
- Raise the body up.
- Keep your head up and look straight ahead.
- Raise one leg as high as possible.
- Hold for as long as possible.
- Lower and raise the other leg.
- Repeat for a total of 3 reps.
Lining Up With A Wall Posture Helper Standing posture is important to proper buttock function. Lining the body up with a wall can help train the body to maintain proper posture. - Find a wall and stand against it from the heels to the back of the head.
- Work the backs of the legs and spine as firmly as possible into the wall.
- Work to get the back of the skull into the wall as well.
- Add some abdominal work by working the waistline inward and upward.
- Hold for up to one minute.
- The alignment is how you want to hold your body.
- As you move off the wall, learn to maintain that posture throughout the day and night.
- Repeat the wall exercise several times for reinforcement.
If aching of the hip, back, or knee is part of daily struggles, working out the gluteal muscles may be the solution. Contact the Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic for a full consultation. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. (2023) Dormant butt syndrome may be to blame for knee, hip and back pain. Martin, H. D., Reddy, M., & Gómez-Hoyos, J. (2015). Deep gluteal syndrome. Journal of hip preservation surgery, 2(2), 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhps/hnv029 Daneshmandi, H., Choobineh, A., Ghaem, H., & Karimi, M. (2017). Adverse Effects of Prolonged Sitting Behavior on the General Health of Office Workers. Journal of lifestyle medicine, 7(2), 69–75. https://doi.org/10.15280/jlm.2017.7.2.69 Campos de Oliveira, L., Gonçalves de Oliveira, R., & Pires-Oliveira, D. A. (2015). Effects of Pilates on muscle strength, postural balance and quality of life of older adults: a randomized, controlled, clinical trial. Journal of physical therapy science, 27(3), 871–876. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.871
Individuals striving to be healthy may not know where or how to start. Can hiring a health coach help individuals start their wellness journey and reach their goals? Hiring A Health Coach It's easy to get caught up in the desire to make changes, but it is another thing to actually set a consistent plan in motion. Hiring a health coach can help individuals understand the information, develop an effective wellness routine that suits their lifestyle, and achieve health and wellness goals. A primary healthcare provider could be a resource and have referrals to reputable health coaches in the area. What Do They Do? Health coaches are experts in helping individuals reach health and wellness goals. This can be: - Reducing stress
- Improving self-care
- Focusing on nutrition
- Starting exercise
- Improving quality of life
A health coach helps create a plan and makes it happen. - Health and wellness coaches use motivational interviewing and evidence-based approaches to empower individuals in their wellness journey. (Adam I Perlman, Abd Moain Abu Dabrh. 2020)
- They help identify areas that need improvement, develop a plan, and encourage the individual all the way like a personal fitness trainer.
- Health coaches work with physicians and/or other health professionals in a clinical setting or as individual providers.
- Their role is to provide a holistic approach to health and wellness.
Services Provided Health coaches can provide and assist with: (Shivaun Conn, Sharon Curtain 2019) - Diet and nutrition
- Exercise, movement
- Sleep
- Mental and emotional health
- Occupational wellness
- Relationship building
- Social skills building
A health coach is someone who helps organize and balance various aspects of an individual's life so they can learn to maintain optimal health. - They will help overcome barriers when struggling.
- A health coach listens and provides support for whatever an individual's goals may be.
- A health coach is there until the goal is reached.
Qualifications It is important to ensure the providers being considered have the necessary qualifications. Because some certification programs offer a focus on specific areas like nutrition, it's recommended to identify what is needed before choosing a health coach. Health coaches do not need a university degree, however, many certifications are affiliated with colleges and have educational partnerships that qualify coursework and award college credits. Training to become a health coach consists of: (Shivaun Conn, Sharon Curtain 2019) - Health
- Fitness
- Goal setting
- Coaching concepts
- Nutritional concepts
- Motivational interviewing
- Stress management
- Changing behaviors
Health Goal Examples Health coaching is not a one-size-fits-all approach. A primary healthcare provider or physician provides a diagnosis and medical plan, and a health coach helps guide and support the individual through the plan. However, hiring a health coach does not require a medical condition to employ services. A few examples of health goals that health coaches address include: - Improving quality of life
- Reducing stress and management
- Lifestyle habits
- Weight loss
- Exercise
- Physical activity
- Emotional and psychological health
- Quitting smoking
Finding a Health Coach A few things to consider. Health Goals - Determine goals and expectations.
- There are many types of health coaches and some may specialize, therefore try to determine the expertise needed to achieve the goals.
Budget - Determine how much money will be invested, as many insurance providers do not cover the cost of a health coach.
- Health coaches may charge between $50 to $300 per session.
- Some will offer packages, memberships, and/or discounts.
Certifications - Look into their certification.
- Is it accredited?
- This will ensure choosing a coach who has received the training and expertise needed to provide quality care.
Compatibility - Consult with potential coaches.
- Ask questions and see if they are compatible with specific health goals.
- Interview as many as needed.
Availability/Location - Virtual sessions, in-person meetings, and/or a combination?
- How long are the sessions?
- Frequency of meetings?
- Finding a coach that is flexible and convenient will help maintain a healthy coach/client relationship.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Perlman, A. I., & Abu Dabrh, A. M. (2020). Health and Wellness Coaching in Serving the Needs of Today's Patients: A Primer for Healthcare Professionals. Global advances in health and medicine, 9, 2164956120959274. https://doi.org/10.1177/2164956120959274 Conn, S., & Curtain, S. (2019). Health coaching as a lifestyle medicine process in primary care. Australian journal of general practice, 48(10), 677–680. https://doi.org/10.31128/AJGP-07-19-4984
Can adding calisthenics resistance training to a fitness routine provide health benefits like flexibility, balance, and coordination? Calisthenics Resistance Training - Calisthenics resistance training requires no equipment, they can be done with minimal space, and are a great way to get a quick burn.
- They are a form of resistance training using your own body weight that is low-impact, which makes it accessible to individuals of all ages and fitness levels.
- They effectively help build agility, and cardiovascular health, and improve balance, coordination, and flexibility.
Benefits Muscle Strength Because calisthenics are easily adaptable to any fitness level, require minimal or no equipment, and are great for beginners and experienced exercise enthusiasts it is a fantastic full-body workout and an excellent way to build strength and muscle. Research supports that calisthenics resistance training can improve muscle strength in various ways. - One study found that eight weeks of calisthenics not only improved posture and body mass index/BMI but can impact strength, even with exercises not routinely performed. (Thomas E, et al., 2017)
- During the study, one group did calisthenics and the other maintained regular training routines.
- The researchers discovered that the group that did calisthenics increased their repetitions of exercises that were not included.
- The group who continued with their regular training routines did not improve on what they could do before the eight-week study. (Thomas E, et al., 2017)
Cardiovascular Fitness - Regular participation in calisthenic resistance training can lead to improved cardiovascular health, including increased endurance and a healthier heart.
- Certain calisthenic exercises, like burpees and mountain climbers, are high-intensity movements that can increase heart rate and blood circulation just from the movements.
- Gradually performing these exercises at a faster pace, research indicates could potentially experience the same cardiovascular benefits from interval or treadmill running. (Bellissimo GF, et al., 2022) - (Lavie CJ, et al., 2015)
Balance, Coordination, and Flexibility - The movements require a full range of motion that stretches and strengthens the muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- These exercises can help decrease the risk of injury and make daily physical activities easier to perform without over-exertion.
- Incorporating calisthenics resistance training on a regular basis can help improve posture, balance, and flexibility, depending on which exercises are recommended.
- Exercises like stretches, lunges, and squats help to improve flexibility and mobility.
- Exercises like single-leg squats and one-arm push-ups can work the balance, coordination, and proprioception of the body.
Mental Health - Exercise, in general, is known to improve mood, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being.
- Calisthenic resistance training can have additional impacts on mental well-being.
- For example, the discipline and focus required to perform the movements can help concentration and mental clarity.
- One study found that calisthenics can reduce cognitive decline and may be useful for dementia prevention. (Osuka Y, et al., 2020)
- Another study found that calisthenics helped mental well-being in individuals with diseases like ankylosing spondylitis and multiple sclerosis. (Taspinar O, et al., 2015)
Types Bodyweight exercises that use an individual's own body weight as resistance are the foundation. Common examples include push-ups, squats, and lunges. An overview of some of the types of exercises. Pulling - These exercises focus on training the muscles for pulling movements, which include the back, shoulders, and arms.
- Examples include pull-ups, chin-ups, and rows.
Pushing - These exercises focus on training the muscles for pushing movements, like the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
- Examples include dips, push-ups, and handstand push-ups.
Core - Core exercises focus on training the abdominal and lower back muscles, which are responsible for maintaining stability and balance.
- Examples of core exercises include planks, sit-ups, and leg raises.
Single-Leg - Single-leg exercises focus on training one leg at a time.
- These target the muscles of the legs, hips, and core.
- Examples of single-leg exercises include single-leg squats, lunges, and step-ups.
Plyometric - Calisthenics resistance training focuses on powerful explosive movements.
- Plyometric exercises challenge the muscles to work quickly and forcefully.
- Examples include jump squats, clap push-ups, and box jumps.
Getting Started - Start by making sure calisthenics is an appropriate workout option, especially if you are a beginner or have pre-existing medical conditions.
- Once cleared to exercise start with familiar movements that can be done with the correct form.
- Pushups, bodyweight squats, planks, lunges, and other basic movements are a good place to start.
- Make sure to warm up with light and easy motions that mimic the workout movements.
- Aim to work each body part during the workout.
- Try for at least two workouts a week.
- It is recommended to split the movement patterns.
- Reps can be counted or set a timer to switch exercises every minute. This is called EMOM-style or every minute on the minute.
- Pick four to five exercises that target various areas.
- For example, sit-ups can be done for the core, lunges for the glutes and thighs, planks can be done for the shoulders and core, and jumping jacks or jumping rope for cardiovascular.
- Calisthenic resistance training is easily modifiable and can be adjusted to individual needs.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Thomas, E., Bianco, A., Mancuso, E. P., Patti, A., Tabacchi, G., Paoli, A., ... & Palma, A. (2017). The effects of a calisthenics training intervention on posture, strength, and body composition. Isokinetics and exercise science, 25(3), 215-222. Bellissimo, G. F., Ducharme, J., Mang, Z., Millender, D., Smith, J., Stork, M. J., Little, J. P., Deyhle, M. R., Gibson, A. L., de Castro Magalhaes, F., & Amorim, F. (2022). The Acute Physiological and Perceptual Responses Between Bodyweight and Treadmill Running High-Intensity Interval Exercises. Frontiers in physiology, 13, 824154. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.824154 Osuka, Y., Kojima, N., Sasai, H., Ohara, Y., Watanabe, Y., Hirano, H., & Kim, H. (2020). Exercise Types and the Risk of Developing Cognitive Decline in Older Women: A Prospective Study. Journal of Alzheimer's disease: JAD, 77(4), 1733–1742. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-200867 Taspinar, O., Aydın, T., Celebi, A., Keskin, Y., Yavuz, S., Guneser, M., Camli, A., Tosun, M., Canbaz, N., & Gok, M. (2015). Psychological effects of calisthenic exercises on neuroinflammatory and rheumatic diseases. Zeitschrift fur Rheumatologie, 74(8), 722–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-015-1570-9 Lavie, C. J., Lee, D. C., Sui, X., Arena, R., O'Keefe, J. H., Church, T. S., Milani, R. V., & Blair, S. N. (2015). Effects of Running on Chronic Diseases and Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 90(11), 1541–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.08.001
Pickleball is a growing, increasingly popular sport that can be enjoyed by individuals of every age and fitness level. It combines elements of tennis and badminton at a slightly slower pace that makes it ideal for families and provides excellent health benefits and enjoyable socializing. It is easy to learn and requires little practice. The sport is easy on the body and is a great activity for seniors because it is joint-friendly. Pickleball Individuals do not need to be athletes or belong to a certain age group to play or benefit from the sport. It requires minimal equipment and a few basic skills. Using a flat paddle and a plastic pickleball, opponents singles or doubles play a game like tennis or badminton. Playing the Game - A three-foot-long net is set up in the center of a court measuring 44 feet long by 20 feet wide.
- The court is divided between right and left service zones.
- If the receiving side misses the serving side volley, the serving side receives a point.
- The game is played to 11 points, but a player or team must win by two points.
- The ball's design keeps the pace manageable and user-friendly.
- Pickleball has other intricacies common with other racket-court sports.
- The player serves from a specific side.
- The no-volley zone, or the kitchen is seven feet from the net on both sides.
- There are rules regarding when the player must call the score, how tournaments work, and variations between singles and doubles matches.
- Most players only need a few games to pick up the basics.
Reasons To Play The sport offers a number of health benefits. Improves Mental Health - One study found individuals who played pickleball tended to have better mental health and outlook.
- Researchers followed older adults competing in pickleball competitions and tournaments.
- At the end of the study, the researchers found that a commitment to a physical hobby correlated to reduced depression levels.
Improves Cardiovascular Health - The sport is not as physically intense as say tennis, but offers significant benefits for cardiovascular health.
- One study found that individuals who played three times a week for an hour had improved cardiorespiratory fitness, lower cholesterol levels, and decreased blood pressure.
- Experts found that it is a healthy alternative to traditional exercises like walking or biking.
Improved Hand-Eye Coordination - Pickleball will improve hand-eye coordination and reflexes.
- Coordinating the feet, legs, arms, hands, and eye movements quickens responses, challenges the brain to think fast, and increases balance.
- Physical activity combined with cognitive challenges has been found to improve cognitive health and prevent mental decline in older adults.
Socialization - Pickleball requires an opponent or two for doubles matches.
- A significant benefit is that the sport provides increased socialization.
- Socializing with others, especially the elderly can help with loneliness.
- Loneliness can negatively impact physical and mental health, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, dementia, and depression.
Getting Started Individuals need minimal gear like paddles, shoes, and balls and knowledge to get started playing. One of the easiest ways to begin is locating a court in the community. This is a great physical activity that can be competitive, but overall it is fun, easy to play, and provides great health benefits. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Casper, Jonathan M, and Jung-Hwan Jeon. “Psychological Connection to Pickleball: Assessing Motives and Participation in Older Adults.” Journal of Aging and physical activity, 1-6. 24 Oct. 2018, doi:10.1123/japa.2017-0381 Cerezuela, Juan-Leandro, et al. “Pickleball and mental health in adults: A systematic review.” Frontiers in psychology vol. 14 1137047. 21 Feb. 2023, doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1137047 Ryu, Jungsu, et al. “Pickleball, Personality, and Eudaimonic Well-Being in Middle-Aged and Older Adults.” Journal of Aging and physical activity vol. 30,5 885-892. 14 Feb. 2022, doi:10.1123/japa.2021-0298 Vitale, Kenneth, and Steven Liu. “Pickleball: Review and Clinical Recommendations for this Fast-growing Sport.” Current sports medicine reports vol. 19,10 (2020): 406-413. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000759 Webber, Sandra C et al. “Physical Activity Intensity of Singles and Doubles Pickleball in Older Adults.” Journal of Aging and physical activity vol. 31,3 365-370. 10 Sep. 2022, doi:10.1123/japa.2022-0194
Working out on a treadmill is a great way to get cardiovascular exercise when unable to go outside or to change things up. However, it's not just about getting on the machine and walking or running. Like anything, proper form and posture are important in preventing injuries. This allows the individual to walk smoother and faster, burn more calories, and get the full benefits. Individuals with a medical condition that impacts posture or makes it difficult to walk on a treadmill should speak to a healthcare provider for recommendations to ensure they can work out without aggravating the condition or putting themselves at risk. There is an option of working with a physical or occupational therapist to address any concerns individuals may have about using a treadmill. Treadmill Walking Exercise Errors Safety A common error is getting on a treadmill with the belt already running. This may seem unnecessary, but many accidents happen when individuals just jump on. To avoid injuries, it is recommended to follow these safety tips. - Make sure the machine is off.
- Know where the emergency stop switch is.
- Stand next to the base/running deck.
- Clip the safety key to your body to stop the treadmill if you slip or stumble.
- Start the treadmill and set it to slow speed.
- Look at the speed and carefully get onto the moving tread.
- Gradually increase the speed once comfortably on board.
Wrong Shoes A healthy step is to strike with the heel in front with the forward foot slightly off the surface. The foot then rolls from heel to toe; by the time the toe is on the ground, the individual is halfway into the next step, and the forward foot is now the rear foot and ready for the toes to push off to take the next step. - This sequence is only possible with flexible shoes.
- Wearing stiff shoes may not allow for the roll-through.
- Stiff shoes force the foot to slap down.
- The body and walking stride become a flat-footed stomp.
- Take a few minutes during a walking session to think about what the feet are doing.
- Ensure they strike with the heel, roll through the step, and the rear foot provides an adequate push-off.
- If you cannot do this in your present shoes, then it's time to look at other flexible walking/running shoes.
Holding The Handrails - The handrails provide stability, but natural walking posture or natural movement involves a healthy stride and arm motion.
- Constantly holding onto the handrails doesn't allow for this motion.
- Walking or running at a slower pace is recommended without using the handrails.
- Individuals will get a better workout at a slower pace than they would at a faster rate holding on to the rails.
- Individuals with a disability or balance issues may need the handrails and should consult a trainer or physical therapist for healthy workout recommendations.
Leaning Forward Proper walking posture means the body is upright, not leaning forward or backward. - Before stepping onto the treadmill, check and readjust your posture.
- Engage the abdominals and maintain a neutral spine.
- Give the shoulders a backward roll so they are not hunched up.
- Get on the treadmill and walk.
- Remind yourself to maintain this upright posture.
- When changing pace or incline, check your posture again.
Looking Down and Not Ahead - A healthy walking posture means the head is up and the eyes forward.
- An unhealthy walking posture can lead to neck, shoulder, and low back pain.
- Improper posture doesn't allow the body to take full, complete breaths.
- It also reinforces unhealthy sitting postures.
- Check the shoulders and do a backward roll every few minutes to ensure they aren't hunching forward.
Overstriding - Overstriding means the front heel hits the ground too far in front of the body.
- Many individuals do this to walk faster.
- An overstride can result in the foot slipping, which can cause a trip and/or a fall.
- A healthy walking stride means the front heel strikes close to the body while the back foot stays on the ground longer to provide a powerful push-off.
- This push-off provides more speed and power and works the muscles better to burn more calories.
- You may need to shorten the stride and take shorter steps when beginning.
- Then focus on feeling the back foot and getting a thorough push with each step.
- Focus on this for a few minutes each session until it becomes familiar and walking becomes faster and easier.
No Arm Movement - If the handrails are not necessary, the arms should be moving during the workout.
- Proper arm motion allows the body to go faster and burn more calories.
- The swinging motion can help shoulder and neck problems developed from unhealthy postures.
- The legs only move as fast as the arms do.
- To speed up the legs, speed up the arms.
Going Too Fast - Go only as fast as the body can go while maintaining proper walking posture and form.
- If overstriding, leaning forward, or hunching shoulders begin to present, slow down until a comfortable/maintainable speed that allows the body to walk correctly is found.
- If the workout doesn't feel like it's helping
- Individuals with a bad walking form at high speeds may consider adding running intervals.
- Running will create quick bursts of higher heart rate and change form.
Running Intervals - Warm up at a slow speed for 3 to 5 minutes.
- Increase walking speed to a fast pace that can maintain proper walking form.
- Start a jog and increase the speed to match the jogging pace.
- Jog for 1 to 3 minutes.
- Return to the fast walking pace for 3 to 5 minutes.
- Jog for 1 to 3 minutes.
- Repeat until the end of the workout.
- Finish with 3 to 5 minutes at an easy walking pace to cool down.
Challenge Yourself When the body has fully adapted to a workout, it's time to challenge the body to achieve greater fitness and stay motivated. This is where workout variation intensity, duration, frequency, and/or mode come into play. Intensity - Add intensity by increasing the incline or the speed.
Duration - Increase the time spent on the treadmill.
- If spending 30 minutes for several weeks, increase to 45 minutes for at least one weekly session.
- After a couple of weeks, increase to 60 minutes.
Frequency - Once the body is used to treadmill walking, try to incorporate a session every day or every other day.
- Walk at a brisk pace for 30 to 60 minutes, going for a total of 150 to 300 minutes per week.
Type of Exercise - Try jogging or running.
- Alternate using the exercise bike, rowing machine, or stair climber.
- Add weight training, circuit training, or anything enjoyable that gets the body moving in different ways.
Set goals and get into the habit of using the treadmill regularly to reap all the benefits. Avoid common treadmill errors, stay safe, and make the most out of walking and running workouts. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Benefits of Physical Activity. Donlin, Margo C et al. "Adaptive treadmill walking encourages persistent propulsion." Gait & Posture vol. 93 (2022): 246-251. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2022.02.017 Donlin, Margo C et al. "User-driven treadmill walking promotes healthy step width after stroke." Gait & Posture vol. 86 (2021): 256-259. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.03.031 Hashiba, M. "Transient change in standing posture after linear treadmill locomotion." The Japanese Journal of Physiology vol. 48,6 (1998): 499-504. doi:10.2170/jjphysiol.48.499 Liang, Junjie et al. "The effect of anti-gravity treadmill training for knee osteoarthritis rehabilitation on joint pain, gait, and EMG: Case report." Medicine vol. 98,18 (2019): e15386. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000015386 MacEwen, Brittany T et al. "A systematic review of standing and treadmill desks in the workplace." Preventive medicine vol. 70 (2015): 50-8. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.11.011
Healthy aging has been linked to a lifestyle consisting of proper nutrition and exercise. However, even with a healthy lifestyle, the body undergoes changes that include conditions, disease, and compromises in physical performance. Because of the effects of aging on muscle and joint tissue, cardiovascular fitness, and other physical parameters, older athletes need to take consideration, but this doesn't mean slowing down. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can develop a training and treatment plan to build and maintain musculoskeletal system health, flexibility, and optimal function. Older Athletes Research has shown that the physical and mental declines that go with aging can be reduced with fitness and nutrition programs and that it is not too late to start improving fitness, no matter what age. Systemic changes that happen to an aging body include: Nervous System - Imbalances happen more easily and more often.
- Sensation changes.
Musculoskeletal System - Bone Strength Decreases.
- Muscle Strength Decreases.
- Flexibility issues occur more frequently.
Respiratory System - Decreased Vital or Breathing Capacity of Lungs - The maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a full inhalation.
Cardiovascular System - Maximum Heart Rate slows down.
- A slower return to resting heart rate after and during physical activity and exercise.
Maintaining Endurance Common aging fitness declines include: - Changes in body composition.
- Increased body fat.
- Decreased muscle mass.
- Loss of height - can be brought on by osteoporosis.
- Diminished cardiorespiratory capacity.
- Muscle atrophy.
Research has found that when seniors start to exercise, their health improves quickly. It's estimated that the physical declines associated with aging are not necessarily inevitable but can also happen by losing fitness/deconditioning effects from reduced exercise levels, frequency, and/or intensity. Despite the losses, older athletes are often able to compete and excel in endurance activities because they tend to have higher proportions of slow twitch fibers. Memory and Fitness - Evidence suggests that seniors who exercise reduce the physical effects of aging and prevent their brain/memory from advanced degeneration.
- Physical fitness has been linked with reduced memory decline in middle-aged adults.
Training Options Training methods to maintain athletic performance. Hill Running or Interval Training - This type of training can improve fitness and condition the aerobic and anaerobic systems.
Weight Training - Weight training maintains muscle tone, fast twitch muscle fibers, and strength.
Plyometric exercises Creatine Supplements - Supplements may help improve performance during repetitive, intense exercise sessions.
Nutrition Aging causes the joints to become less flexible, resulting in a range of motion loss leading to limitations and compromised physical abilities. Proper nutrition in older athletes can protect the joints and prevent advanced degeneration. The following nutrients are recommended: - Omega-3's - nuts, seeds, and fatty fish provide anti-inflammatory effects.
- Vitamin C for collagen production.
- Sulfur amino acids - certain vegetables, meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products improve joint cartilage health.
- Bioflavonoids - all fruit and vegetables provide anti-inflammatory effects and improved circulation.
- Antioxidants - selenium and vitamin E protect against free radicals that multiply with age.
- Supplements may also be helpful but check with a doctor before beginning a program.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Gillis, Angela, and Brenda MacDonald. "Deconditioning in the hospitalized elderly." The Canadian nurse vol. 101,6 (2005): 16-20. Lexell, J. "Human aging, muscle mass, and fiber type composition." The Journal of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and medical sciences vol. 50 Spec No (1995): 11-6. doi:10.1093/gerona/50a.special_issue.11 Marriott, Catherine F S, et al. "High-Intensity Interval Training in Older Adults: a Scoping Review." Sports medicine - open vol. 7,1 49. 19 Jul. 2021, doi:10.1186/s40798-021-00344-4 Rogers, Michael E et al. "Balance training for the older athlete." International Journal of sports physical therapy vol. 8,4 (2013): 517-30. Tayrose, Gregory A et al. "The Master's Athlete: A Review of Current Exercise and Treatment Recommendations." Sports Health vol. 7,3 (2015): 270-6. doi:10.1177/1941738114548999 Townsend, Danyelle M et al. "Sulfur-containing amino acids and human disease." Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy vol. 58,1 (2004): 47-55. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2003.11.005 Van Roie, Evelien, et al. "An age-adapted plyometric exercise program improves dynamic strength, jump performance and functional capacity in older men either similarly or more than traditional resistance training." PloS one vol. 15,8 e0237921. 25 Aug. 2020, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0237921 Wu, Tingting, and Yanan Zhao. "Associations between functional fitness and walking speed in older adults." Geriatric nursing (New York, N.Y.) vol. 42,2 (2021): 540-543. doi:10.1016/j.gerinurse.2020.10.003
Mountain biking is a recommended sport for building muscle power and strength, endurance, and agility. Mountain biking uses bicycles designed to ride off-road and over rough terrain. The sport requires core strength, endurance, balance, and self-reliance. This is because riders are often far from civilization. Riders must learn to repair broken bike parts and fix flat tires to avoid being stranded. Mountain biking gear that riders carry includes a heavy-duty backpack with plenty of water, food, tools for repairs, and a first aid kit. Using the appropriate gear and equipment will help make the next ride safer and more comfortable. Mountain Biking Gear The first piece of equipment is a properly fitting and well-maintained mountain bike. There are all types of bicycles for every type of rider and trail. There are variations of bikes with full suspension, front suspension, disc brakes, V-brakes, different wheel sizes, and frame materials. It is recommended to consult a professional or visit a bicycle shop specializing in mountain biking to match the individual with the best bike. The right bike makes for a better ride. Brakes - Disc brakes offer more secure braking when going high speed and needing the option to stop safely and at the proper distance.
Frame Size - The bike's frame must be properly set up so the individual can easily step over and pedal at the correct height.
Suspension - Individuals that plan on taking on all kinds of terrains need the bike to absorb the shock and impact and are recommended to consider a full-suspension bike or one with a suspension fork.
Wheels - Mountain bike wheels range in size from 26 to 29 inches, and depending on the terrain and speeds, the right wheel diameter is key.
- Larger wheels accelerate slower but provide improved traction.
- Smaller wheels are lighter and easier to maneuver.
Helmet A helmet is the most important safety gear that significantly reduces the severity of head injuries; no one should ride without one. Mountain bike helmets generally have a visor to help block the sun when riding so individuals can focus on the trail and not be distracted by glare. Three styles of mountain bike helmets are available, depending on the type of activity. XC or Cross Country - Cross-country helmets provide ventilation, are open-faced, and are lightweight.
- These helmets are recommended for long rides.
Trail - A trail mountain biking helmet covers part of the face and has a visor to help protect the head from the sun and other weather elements.
- Trail helmets are recommended for mountain biking, road, and trail cycling.
Full-Face - Full-face helmets are essential for downhill trails at high speeds and on varying terrains.
- They feature an adjustable visor and chin protection for added safety.
Eye Protection - Eye protection helps keep dirt, dust, and debris out of the eyes and helps have clear vision in dark shadows and bright sunlight.
- Glasses or goggles protect the eyes if not using a full-face helmet.
- Choosing a frame with an interchangeable lens system that comes with different lenses for varying light conditions is recommended.
Hydration Pack - Wearing a hydration pack when riding provides easy access to hands-free hydration.
- This is important for anyone exercising for more than two hours and with limited access to refills on the trail.
Mountain Biking Shoes - Beginners can wear comfortable sports shoes when starting.
- Riders who begin riding more frequently will eventually want to transition to mountain biking shoes.
- Cleated bike shoes work with pedals and lock the rider's feet to the bike.
- There is a variety of cycling footwear, but all-mountain bike shoes provide thorough traction off the bike, durability, comfort, and a heavy-duty sole for optimal pedaling efficiency.
Clipless Pedals - Clipless pedals are recommended for cross-country trail riding.
- Cycling shoes and clipless pedal systems lock the shoes into the pedals for secure and efficient pedaling and can be unclipped easily with a twist of the foot.
- Use shoes and pedals that work together.
Gloves - Mountain bike gloves provide additional padding and finger coverage.
- They absorb the shock and protect the hands from falls on rough terrain.
- The handlebar grips are padded, but additional cushion from the gloves is beneficial for long or downhill rides for extra comfort and protection.
- Full-finger gloves offer the best coverage, protection, and grip on the brake levers.
Padded Bike Shorts - Padded and protective bike shorts offer benefits for riding long distances and over rough terrain.
- These shorts provide a padded inner liner like underwear that increases comfort and reduces chafing.
- The exterior looks like a baggy pair of shorts made of tough, abrasion-resistant fabric to take the wear and tear.
Bicycle Repair Kit - A repair kit can be attached to the bike saddle and holds all the essential tools for mechanical trouble or a flat tire.
- The repair kit should include a bicycle multi-tool, an extra tube and patch kit, tire levers, a mini pump, and emergency cash.
- Riders should keep an identification card with a list of contact numbers in the seat bag in case of a serious injury or other emergencies.
First Aid Kit - Riders can lose traction on loose rock and crash on the trail.
- A first aid kit with various bandages, tape, pain relievers, and antiseptic wipes to treat cuts, scrapes, blisters, rashes, and everything in between is highly recommended.
- Also include an eye drop solution, a small pocketknife, moleskin, energy gels, and an emergency whistle.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Alena Høye, Bicycle helmets – To wear or not to wear? A meta-analysis of the effects of bicycle helmets on injuries, Accident Analysis & Prevention, Volume 117, 2018, Pages 85-97, ISSN 0001-4575, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2018.03.026. Ansari, Majid, et al. "Mountain Biking Injuries." Current sports medicine reports vol. 16,6 (2017): 404-412. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000429 Clark, Gregory, et al. "Do Mountain Bikers Know When They Have Had a Concussion and, Do They Know to Stop Riding?." Clinical Journal of sports medicine: official journal of the Canadian Academy of Sports Medicine vol. 31,6 (2021): e414-e419. doi:10.1097/JSM.0000000000000819 Hall, Cougar et al. "Pedal-Assist Mountain Bikes: A Pilot Study Comparison of the Exercise Response, Perceptions, and Beliefs of Experienced Mountain Bikers." JMIR formative research vol. 3,3 e13643. 13 Aug. 2019, doi:10.2196/13643 Impellizzeri, Franco M, and Samuele M Marcora. "The physiology of mountain biking." Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 37,1 (2007): 59-71. doi:10.2165/00007256-200737010-00005 Kronisch, R.L., Pfeiffer, R.P. Mountain Biking Injuries. Sports Med 32, 523–537 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232080-00004
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
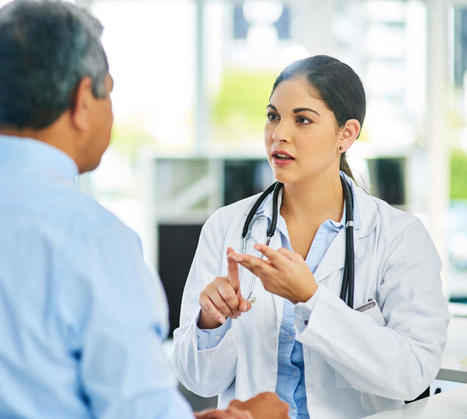

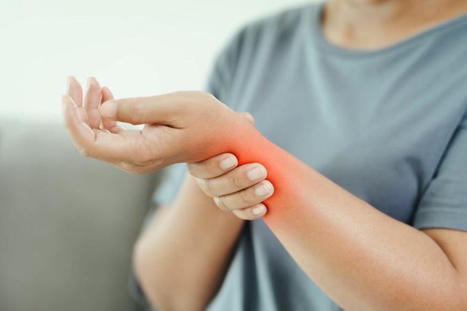






























Can various stretches be beneficial for individuals dealing with wrist and hand pain by reducing pain and discomfort to the extremities? If you have any questions or concerns, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.