 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
For individuals who are dealing with constant constipation due to medications, stress, or lack of fiber, can walking exercise help encourage regular bowel movements? Walking For Constipation Assistance Constipation is a common condition. Too much sitting, medications, stress, or not getting enough fiber can result in infrequent bowel movements. Lifestyle adjustments can regulate most cases. One of the most effective ways is to incorporate regular moderate-vigorous exercise, encouraging the bowel muscles to contract naturally (Huang, R. et al., 2014). This includes jogging, yoga, water aerobics, and power or brisk walking for constipation alleviation. The Research A study analyzed middle-aged obese women who had chronic constipation over a 12-week period. (Tantawy, S. A., et al., 2017) - The first group walked on a treadmill 3 times a week for 60 minutes.
- The second group did not engage in any physical activity.
- The first group had greater improvement in their constipation symptoms and quality of life assessments.
A gut bacteria imbalance is also linked to constipation issues. Another study focused on the effect of brisk walking versus exercises that strengthened core muscles like planks on intestinal microbiota composition. (Morita, E., et al., 2019) The results showed that aerobic exercises like power/brisk walking can help increase intestinal Bacteroides, an essential part of healthy gut bacteria. Studies have shown a positive effect when individuals engage in at least 20 minutes of brisk walking daily. (Morita, E., et al., 2019) Exercise Can Help Decrease Colon Cancer Risks Physical activity can be a significant protective factor in decreasing colon cancer. (National Cancer Institute. 2023) Some estimate the risk reduction to be 50%, and exercise can even help prevent recurrence after a colon cancer diagnosis, also 50% in some studies for patients with stage II or stage III colon cancer. (Schoenberg M. H. 2016) - The best effects were obtained through moderate-intensity exercise, such as power/brisk walking, about six hours per week.
- Mortality was reduced by 23% in individuals who were physically active for at least 20 minutes several times a week.
- Inactive colon cancer patients who began exercising after their diagnosis had significantly improved outcomes than individuals who remained sedentary, showing that it is never too late to start exercising.(Schoenberg M. H. 2016)
- The most active patients had the best outcomes.
Exercise-Related Diarrhea Prevention Some runners and walkers experience an overly active colon, resulting in exercise-related diarrhea or loose stools, known as runner's trots. Up to 50% of endurance athletes experience gastrointestinal problems during intense physical activity. (de Oliveira, E. P. et al., 2014) Prevention steps that can be taken include. - Not eating within two hours of exercising.
- Avoid caffeine and warm fluids before exercising.
- If sensitive to lactose, avoid milk products or use Lactase.
- Ensure the body is well-hydrated before exercise.
- Hydrating during exercise.
If exercising in the morning: - Drink about 2.5 cups of fluids or a sports drink before bed.
- Drink about 2.5 cups of fluids after waking up.
- Drink another 1.5 - 2.5 cups of fluids 20-30 minutes before exercising.
- Drink 12-16 fluid ounces every 5-15 minutes during exercise.
If exercising for over 90 minutes: - Drink a 12 - 16 fluid-ounce solution containing 30-60 grams of carbohydrates, sodium, potassium, and magnesium every 5-15 minutes.
Professional Help Periodic constipation may resolve with lifestyle adjustments like increased fiber intake, physical activity, and fluids. Individuals who are experiencing bloody stools or hematochezia, have recently lost 10 pounds or more, have iron deficiency anemia, have positive fecal occult/hidden blood tests, or have a family history of colon cancer need to see a healthcare provider or specialist to perform specific diagnostic tests to ensure there aren't any underlying issues or serious conditions. (Jamshed, N. et al., 2011) Before engaging in walking for constipation assistance, individuals should consult their healthcare provider to see if it is safe for them. At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, our areas of practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols. We focus on what works for you to achieve improvement goals and create an improved body through research methods and total wellness programs. If other treatment is needed, individuals will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited to their injury, condition, and/or ailment. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Huang, R., Ho, S. Y., Lo, W. S., & Lam, T. H. (2014). Physical activity and constipation in Hong Kong adolescents. PloS one, 9(2), e90193. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090193 Tantawy, S. A., Kamel, D. M., Abdelbasset, W. K., & Elgohary, H. M. (2017). Effects of a proposed physical activity and diet control to manage constipation in middle-aged obese women. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity: targets and therapy, 10, 513–519. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S140250 Morita, E., Yokoyama, H., Imai, D., Takeda, R., Ota, A., Kawai, E., Hisada, T., Emoto, M., Suzuki, Y., & Okazaki, K. (2019). Aerobic Exercise Training with Brisk Walking Increases Intestinal Bacteroides in Healthy Elderly Women. Nutrients, 11(4), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040868 National Cancer Institute. (2023). Colorectal Cancer Prevention (PDQ(R)): Patient Version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colorectal-prevention-pdq
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26389376 Schoenberg M. H. (2016). Physical Activity and Nutrition in Primary and Tertiary Prevention of Colorectal Cancer. Visceral medicine, 32(3), 199–204. https://doi.org/10.1159/000446492 de Oliveira, E. P., Burini, R. C., & Jeukendrup, A. (2014). Gastrointestinal complaints during exercise: prevalence, etiology, and nutritional recommendations. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 44 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), S79–S85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0153-2 Jamshed, N., Lee, Z. E., & Olden, K. W. (2011). Diagnostic approach to chronic constipation in adults. American Family Physician, 84(3), 299–306.
Individuals with digestive problems that cannot be diagnosed could be experiencing functional gastrointestinal disorders. Could understanding the types help in developing effective treatment plans? Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Functional gastrointestinal disorders, or FGDs, are disorders of the digestive system in which the presence of structural or tissue abnormality cannot explain symptoms. Functional gastrointestinal disorders lack identifiable biomarkers and are diagnosed based on symptoms. (Christopher J. Black, et al., 2020) Rome Criteria FGDs used diagnoses of exclusion, meaning that they could only be diagnosed after organic/identifiable disease was ruled out. However, in 1988, a group of researchers and healthcare providers met to devise strict criteria for the diagnosis of the various types of FGDs. The criteria is known as the Rome Criteria. (Max J. Schmulson, Douglas A. Drossman. 2017) FGDs A comprehensive list as described by the Rome III criteria (Ami D. Sperber et al., 2021) Functional Esophageal Disorders - Functional heartburn
- Functional chest pain believed to be of esophageal origin
- Functional dysphagia
- Globus
Functional Gastroduodenal Disorders - Unspecified excessive belching
- Functional dyspepsia - includes postprandial distress syndrome and epigastric pain syndrome.
- Chronic idiopathic nausea
- Aerophagia
- Functional vomiting
- Cyclic vomiting syndrome
- Rumination syndrome in adults
Functional Bowel Disorders - Irritable bowel syndrome - IBS
- Functional constipation
- Functional diarrhea
- Unspecified functional bowel disorder
Functional Abdominal Pain Syndrome - Functional abdominal pain - FAP
Functional Gallbladder and Sphincter of Oddi Disorders - Functional gallbladder disorder
- Functional biliary Sphincter of Oddi disorder
- Functional pancreatic Sphincter of Oddi disorder
Functional Anorectal Disorders - Functional fecal incontinence
- Functional Anorectal Pain - includes chronic proctalgia, Levator ani syndrome, unspecified functional anorectal pain, and proctalgia fugax.
- Functional Defecation Disorders - include dyssynergic defecation and inadequate defecatory propulsion.
Childhood Functional GI Disorders Infant/Toddler (Jeffrey S. Hyams et al., 2016) - Infant colic
- Functional constipation
- Functional diarrhea
- Cyclic vomiting syndrome
- Infant regurgitation
- Infant rumination syndrome
- Infant dyschezia
Childhood Functional GI Disorders: Child/Adolescent - Vomiting and Aerophagia - cyclic vomiting syndrome, adolescent rumination syndrome, and aerophagia
- Abdominal Pain-Related Functional GI Disorders include:
- functional dyspepsia
- IBS
- Abdominal migraine
- Childhood functional abdominal pain
- Childhood functional abdominal pain syndrome
- Constipation - functional constipation
- Incontinence - nonretentive fecal incontinence
Diagnosis Although the Rome criteria allow the diagnosis of FGDs to be symptom-based, a healthcare provider may still run standard diagnostic tests to rule out other diseases or look for structural problems resulting in symptoms. Treatment Although no visible signs of disease or structural problems may be identified as causing the symptoms, it does not mean that they are not treatable and manageable. For individuals who suspect they may have or have been diagnosed with a functional gastrointestinal disorder, it will be essential to work with a healthcare provider on a working treatment plan. Treatment options can include: (Asma Fikree, Peter Byrne. 2021) - Physical therapy
- Nutritional and dietary adjustments
- Stress management
- Psychotherapy
- Medication
- Biofeedback
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Black, C. J., Drossman, D. A., Talley, N. J., Ruddy, J., & Ford, A. C. (2020). Functional gastrointestinal disorders: advances in understanding and management. Lancet (London, England), 396(10263), 1664–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32115-2 Schmulson, M. J., & Drossman, D. A. (2017). What Is New in Rome IV. Journal of neurogastroenterology and motility, 23(2), 151–163. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm16214 Sperber, A. D., Bangdiwala, S. I., Drossman, D. A., Ghoshal, U. C., Simren, M., Tack, J., Whitehead, W. E., Dumitrascu, D. L., Fang, X., Fukudo, S., Kellow, J., Okeke, E., Quigley, E. M. M., Schmulson, M., Whorwell, P., Archampong, T., Adibi, P., Andresen, V., Benninga, M. A., Bonaz, B., … Palsson, O. S. (2021). Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology, 160(1), 99–114.e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.014 Hyams, J. S., Di Lorenzo, C., Saps, M., Shulman, R. J., Staiano, A., & van Tilburg, M. (2016). Functional Disorders: Children and Adolescents. Gastroenterology, S0016-5085(16)00181-5. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.015 Fikree, A., & Byrne, P. (2021). Management of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Clinical medicine (London, England), 21(1), 44–52. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmed.2020-0980
Individuals need to eat more fiber for optimal gut health. Can adding avocado to their diet help improve the gut microbe diversity? Avocado Gut Support A diverse gut microbiome is beneficial to overall health. According to a recent study, eating one avocado a day can help maintain the gut microbes healthy, diverse, and balanced. (Sharon V. Thompson, et al., 2021) The researchers observed positive changes in gut bacteria and increased bacterial diversity in individuals who consumed an avocado every day for 12 weeks. (Susanne M Henning, et al., 2019) Gut Diversity The gut microbiome refers to the microorganisms living in the intestines. There are around 100 trillion microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and more, exist in the gastrointestinal tract. (Ana M. Valdes, et al., 2018) Having a diverse microbiome means that the body has a range of different organisms that offer various health benefits. Not having enough bacterial diversity has been linked to: (Ana M. Valdes, et al., 2018) - Arthritis
- Obesity
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Celiac disease
- Arterial stiffness
- Atopic eczema
Why Avocados? - The Institute of Medicine recommends a daily fiber intake ranging from 19 grams to 38 grams per day, depending on various factors like age. (Diane Quagliani, Patricia Felt-Gunderson. 2016)
- Approximately 95% of adults and children do not consume the recommended amount of fiber. (Diane Quagliani, Patricia Felt-Gunderson. 2016)
- Including foods like avocados in a healthy diet can help meet daily fiber requirements.
- Fruit fiber like pectin, has been shown to promote a healthy gut microbiome as well. (Beukema M, et al., 2020)
- Researchers suggest this could be because of pectin's positive effect on beneficial probiotics.(Nadja Larsen, et al., 2018)
- Although further research is needed fiber is believed to help protect the lining of the colon by increasing the bulk and weight of stool and expediting elimination.
- Fiber also adds bulk to an individual's diet and slows the speed of digestion, which makes the body feel fuller longer.
Improved Gut Individuals can support a healthy microbiota by making small adjustments in their diet, including: - Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables with the skin, as this is where a majority of the nutrition is.
- Fermented foods like yogurt, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kefir.
- Limiting consumption of processed foods, sugar, and artificial sweeteners.
- More whole-grain foods.
Ways to eat more avocados include adding them to: - Smoothies
- Salads
- Sandwichs
- Guacamole
- If there are more avocados that can be eaten before they overripen, they can be frozen.
- Peel and slice them first, then place them in freezer bags to have year-round.
- They are rich in healthy fat, however, in moderation, they are not likely to contribute to weight gain.
Individuals can work toward having a diverse gut microbiome by paying attention to the foods they eat. Specific foods and dietary patterns can influence the different types of bacterial diversity which can support health. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Thompson, S. V., Bailey, M. A., Taylor, A. M., Kaczmarek, J. L., Mysonhimer, A. R., Edwards, C. G., Reeser, G. E., Burd, N. A., Khan, N. A., & Holscher, H. D. (2021). Avocado Consumption Alters Gastrointestinal Bacteria Abundance and Microbial Metabolite Concentrations among Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. The Journal of nutrition, 151(4), 753–762. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxaa219 Henning, S. M., Yang, J., Woo, S. L., Lee, R. P., Huang, J., Rasmusen, A., Carpenter, C. L., Thames, G., Gilbuena, I., Tseng, C. H., Heber, D., & Li, Z. (2019). Hass Avocado Inclusion in a Weight-Loss Diet Supported Weight Loss and Altered Gut Microbiota: A 12-Week Randomized, Parallel-Controlled Trial. Current developments in nutrition, 3(8), nzz068. https://doi.org/10.1093/cdn/nzz068 Valdes, A. M., Walter, J., Segal, E., & Spector, T. D. (2018). Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 361, k2179. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2179 Quagliani, D., & Felt-Gunderson, P. (2016). Closing America's Fiber Intake Gap: Communication Strategies From a Food and Fiber Summit. American journal of lifestyle medicine, 11(1), 80–85. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827615588079 Beukema, M., Faas, M. M., & de Vos, P. (2020). The effects of different dietary fiber pectin structures on the gastrointestinal immune barrier: impact via gut microbiota and direct effects on immune cells. Experimental & molecular medicine, 52(9), 1364–1376. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0449-2 Larsen, N., Cahú, T. B., Isay Saad, S. M., Blennow, A., & Jespersen, L. (2018). The effect of pectins on survival of probiotic Lactobacillus spp. in gastrointestinal juices is related to their structure and physical properties. Food microbiology, 74, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2018.02.015
Should individuals with existing gastrointestinal problems eat bananas? Bananas - Bananas can be easy to digest and are often recommended for nausea and diarrhea, however, not everyone can tolerate them. (MedlinePlus. 2021)
- Bananas are high in fructose, sorbitol, and soluble fiber, which makes them a common trigger for gastrointestinal problems.
- Additionally, individuals not used to eating a high-fiber diet may find it helpful to gradually increase fiber and drink more water to alleviate unpleasant symptoms.
- If there is a suspicion of intolerance, IBS, or malabsorption, it is recommended to speak with a healthcare provider for an evaluation.
- Bananas can make the stomach hurt due to:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Cramping
- Gas
- Bloating
- Other gastrointestinal (GI) problems.
- Individuals can experience stomach discomfort if there is a fructose intolerance or a rare banana allergy.
Stomach Pain - Bananas are used to replenish potassium and other essential nutrients lost from vomiting or diarrhea.
- Some individuals can experience bloating and gas after eating them.
- One reason is because of their soluble fiber content.
- Soluble fiber dissolves in water and is more readily fermented in the colon than insoluble fiber.
- This can lead to gas and bloating. (Jackson Siegelbaum Gastroenterology. 2018)
- Bananas also contain sorbitol - a naturally occurring sugar that acts as a laxative and can cause gas, bloating, and diarrhea when consumed in large amounts. (U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2023)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome - IBS - Bananas can be a common trigger food for individuals with IBS.
- This is because as bananas break down in the stomach, they can generate excess gas. (Bernadette Capili, et al., 2016)
- Bananas are also high in fructose/simple sugar especially when they have overripened.
- Individuals who have IBS are advised to avoid bananas because they can trigger many of the same side effects as undigested lactose/sugar in milk. (Johns Hopkins Medicine. 2023)
- Ripe bananas are considered to be high in FODMAPS - fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols.
- Individuals following a low FODMAP diet to manage IBS may want to avoid or limit consumption.
- Unripe bananas are considered to be low-FODMAP food. (Monash University. 2019)
Allergy - Banana allergies are rare and affect less than 1.2% of the global population.
- Many individuals with a banana allergy are also allergic to pollen or latex because of similar protein structures. (Dayıoğlu A, et al., 2020)
- An individual with a banana allergy may experience wheezing, narrowing of the throat, or hives within minutes of eating.
- They can also experience nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. (Family Medicine Austin. 2021)
Fructose Intolerance - An individual with fructose intolerance has difficulty digesting fructose.
- Individuals with this intolerance should restrict or limit fructose. (UW School of Medicine and Public Health. 2019)
- Fructose malabsorption is when the body cannot digest or absorb fructose correctly. This causes bloating gas and abdominal discomfort.
- Hereditary fructose intolerance is very rare. It happens when the liver cannot assist in the breakdown of fructose.
- This condition often causes more severe symptoms and requires additional treatment besides removing fructose from an individual's diet. (UW School of Medicine and Public Health. 2019)
- Most can tolerate small amounts of fructose found in fruits like bananas.
- There is often more difficulty tolerating large fructose amounts found in honey and high fructose corn syrup. (UW School of Medicine and Public Health. 2019)
Prevent GI Symptoms - If experiencing gas, bloating, or abdominal discomfort after eating bananas, consider limiting the portion size.
- For example, instead of eating one or more bananas a day, try eating half of a banana to see if symptoms resolve.
- Alternatively, if there is a belief that there is fructose malabsorption, try temporarily removing all high-fructose foods.
- If the body begins to feel better, slowly add foods that contain fructose.
- This can help you pinpoint the foods that are causing the problem. (UW School of Medicine and Public Health. 2019)
- If you're eating bananas that are too green or unripe, you may also experience stomach discomfort.
- Unripened bananas contain high amounts of resistant starch. In large quantities, this can cause mild symptoms like gas and bloating. (Jennifer M Erickson, et al., 2018)
- Resistant starch ferments slowly, so it usually does not cause as much gas as other fiber types. (The Johns Hopkins Guide to Diabetes. 2020)
- Ripe or cooked bananas have less starch and more simple sugars, making them easier to digest. (University of Hawaii. 2006)
- Drinking more water and gradually increasing fiber intake can also reduce GI side effects. (The Johns Hopkins Guide to Diabetes. 2020)
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References MedlinePlus. Bananas and nausea. Jackson Siegelbaum Gastroenterology. Colon gas and flatus prevention. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Sorbitol. Capili, B., Anastasi, J. K., & Chang, M. (2016). Addressing the Role of Food in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptom Management. The journal for nurse practitioners: JNP, 12(5), 324–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurpra.2015.12.007 Johns Hopkins Medicine. 5 foods to avoid if you have IBS. Monash University. Bananas re-tested. Dayıoğlu A, Akgiray S, Nacaroğlu HT, Bahçeci Erdem S. The clinical spectrum of reactions due to banana allergy. BMB. 2020;5(2):60-63. doi: 10.4274/BMB.galenos.2020.04.013 Family Medicine Austin. Banana allergy. UW School of Medicine and Public Health. Fructose-restricted diet. Erickson, J. M., Carlson, J. L., Stewart, M. L., & Slavin, J. L. (2018). The Fermentability of Novel Type-4 Resistant Starches in In Vitro System. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 7(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7020018 The Johns Hopkins Guide to Diabetes. What is resistant starch? The University of Hawaii. Cooking banana.
Pesto is a sauce that is made with garlic, pine nuts, basil, cheese, and olive oil, which creates a strong, rich flavor. It is used as a marinade, dip, salad dressing, sandwich spread, and a topping for dishes like pasta and pizza. It can be homemade or bought premade, including vegan varieties. It is made with nutritious ingredients and can be consumed as part of a balanced diet. The sauces can vary in nutrition, but in general, it is a rich source of healthy fats and is also part of the Mediterranean Diet. Pesto Carbohydrates - The sauce is not a significant source of complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber, or sugar.
- A spoonful contains under 1 gram of carbohydrates.
- It is often paired with foods rich in carbohydrates, like sandwiches, pizza, and pasta.
Fats - Nearly 60% of the calories in pesto come from fats, provided by the olive oil, cheese, and pine nuts.
- There are 9.47 grams of fats per spoonful, which includes:
- 5.63 grams of monounsaturated fatty acids.
- 1.53 grams of saturated fatty acids.
- 1.68 grams of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- It also contains 2.56mg of cholesterol.
- According to U.S. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 20% to 35% of daily calories should come from fat.
Protein - The sauce is not a protein-rich food with only 1.38 grams of protein per tablespoon.
- It is often used as a condiment, it can add flavor to other foods higher in protein.
Vitamins and Minerals - Pesto contains:
- 33.1mg of calcium.
- 36.8mg of phosphorus.
- 31.8mg of potassium.
- 9.76mg of magnesium.
Health Benefits Some of the potential health benefits of pesto. Antioxidant Properties - Garlic, pine nuts, olive oil, and basil are rich sources of antioxidants.
- Antioxidants have an essential role in defending the body against free radical damage, which can lead to disease.
- Diets high in antioxidants reduce the risk of various diseases, like heart disease and cancer.
- Consuming antioxidant-rich foods like pesto on a regular basis can increase antioxidant levels.
Cardiovascular Benefits - Olive oil health benefits include the reduced risk of heart disease.
- Substituting other high-fat foods like margarine, butter, and mayonnaise with olive oil can help lower the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Help Lower Cholesterol - Four different types of fats - saturated, trans, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats.
- Saturated fats can raise LDL/unhealthy cholesterol levels.
- Foods rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats like pesto can help lower LDL cholesterol levels in the blood and support HDL/healthy cholesterol levels.
Weight Management - Pesto is commonly consumed on the Mediterranean diet and can be part of a nutritious lifestyle that supports a healthy weight.
- Research has shown that following a Mediterranean diet can lead to and maintain long-term changes in weight management.
- Store-bought pesto can contain a large amount of sodium.
- Individuals following a low-sodium diet or taking heart medications should check with their doctor before consuming these products.
- To control the amount of sodium, consider making a homemade recipe that uses less salt and aligns with individual dietary preferences.
Types - Grocery stores generally carry several varieties of pesto.
- Basil is the main ingredient but some varieties are made with other herbs.
- Pesto traditionally contains parmesan cheese/milk products and pine nuts/tree nuts which are common food allergens.
- The sauce is a vegetarian-friendly sauce, but vegans can look for cheese and dairy-free versions.
- It is possible that an allergic reaction can occur in individuals allergic to dairy products and nuts.
- Individuals allergic to nuts can choose nut-free varieties.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Agnoli C, Sieri S, Ricceri F, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and long-term changes in weight and waist circumference in the EPIC-Italy cohort. Nutr Diabetes. 2018;8(1):22. doi:10.1038/s41387-018-0023-3 Bolling, Bradley W et al. “Tree nut phytochemicals: composition, antioxidant capacity, bioactivity, impact factors. A systematic review of almonds, Brazils, cashews, hazelnuts, macadamias, pecans, pine nuts, pistachios, and walnuts.” Nutrition research reviews vol. 24,2 (2011): 244-75. doi:10.1017/S095442241100014X Bower, Allyson, et al. “The Health Benefits of Selected Culinary Herbs and Spices Found in the Traditional Mediterranean Diet.” Critical Reviews in food science and nutrition vol. 56,16 (2016): 2728-46. doi:10.1080/10408398.2013.805713 Guasch-Ferré M, Liu G, Li Y, et al. Olive oil consumption and cardiovascular risk in U.S. adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(15):1729-1739. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.02.036 Liu, Qing, et al. “Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Spices.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 18,6 1283. 16 Jun. 2017, doi:10.3390/ijms18061283 Marcelino, Gabriela et al. “Effects of Olive Oil and Its Minor Components on Cardiovascular Diseases, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota.” Nutrients vol. 11,8 1826. 7 Aug. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11081826 Nicastro, Holly L, et al. “Garlic and onions: their cancer prevention properties.” Cancer prevention research (Philadelphia, Pa.) vol. 8,3 (2015): 181-9. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0172 Sestili, Piero, et al. “The potential effects of Ocimum basilicum on health: a review of pharmacological and toxicological studies.” Expert opinion on drug metabolism & toxicology vol. 14,7 (2018): 679-692. doi:10.1080/17425255.2018.1484450 Sun, Liangzi, et al. “Tryptophan targeted pulsed electric field treatment for enhanced immune activity in pine nut peptides.” Journal of food biochemistry vol. 44,6 (2020): e13224. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13224 USDA FoodData Central. Pesto sauce.
Not getting enough fiber in one's diet can lead to fiber deficiency. Fiber helps support gut and microbiome health. Individuals not getting enough fiber may experience irregular bowel movements, constipation, blood sugar fluctuations, not feeling full/satisfied after eating, or rising cholesterol levels. About 100 trillion microorganisms in the gut are integral to maintaining a healthy immune system. Fiber is the food these microorganisms eat that helps them to do their job. Without the proper amount, the immune system's health may also be compromised. Fiber and Gut Health Fiber and gut health benefits include regulating the body's sugars, helping to keep hunger and blood sugar in check, helping to maintain a healthy weight, its ability to prevent or relieve constipation, reduce the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. - Dietary fiber, or roughage, is the part of plant foods the body can't digest or absorb.
- It passes through the stomach, small intestine, and colon and out of the body.
- It is found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Soluble and insoluble forms are important to overall health.
Types Soluble Fiber - This type dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance.
- It can help lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels.
- It is found in oats, peas, beans, apples, citrus fruits, carrots, and barley.
Insoluble Fiber - This type of fiber promotes the movement of material through the digestive system.
- It increases stool bulk, benefiting individuals who struggle with constipation or irregular stools.
- Whole-wheat flour, wheat bran, nuts, beans, and vegetables, such as cauliflower, green beans, and potatoes, are good sources.
Benefits Healthy Bowel Movements - Dietary fiber increases stool weight and thickness and makes it soft.
- Fiber helps to solidify the stool by absorbing water and adding bulk.
- A thicker stool is easier to pass, decreasing the potential for constipation and other problems.
Maintains Bowel Health - A high-fiber diet can lower the risk of developing hemorrhoids and small pouches in the colon/diverticular disease.
- Studies have also found that a high-fiber diet can help lower the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Some fiber gets fermented in the colon.
- Researchers are looking at how this can help prevent diseases of the colon.
Lowers Cholesterol - Soluble fiber found in beans, oats, flaxseed, and oat bran can help lower blood cholesterol levels by lowering low-density lipoprotein or unhealthy cholesterol levels.
- Studies also have shown that high-fiber foods can help reduce blood pressure and inflammation.
Regulates Blood Sugar Levels - In individuals with diabetes, fiber, particularly soluble fiber, can slow the absorption of sugar and improve blood sugar levels.
- A healthy nutrition plan that includes insoluble fiber can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Helps Achieve Healthy Weight - High-fiber foods can be more filling than low-fiber foods, helping individuals eat less and stay satisfied.
- High-fiber foods can also take longer to eat and are less energy dense, meaning they have fewer calories.
Getting More Fiber Ideas for adding more fiber to meals and snacks: Fiber to Start The Day - Choose a high-fiber breakfast cereal with five or more grams of fiber per serving.
- Choose cereals with whole grain, bran, or fiber in the name.
- Add a few tablespoons of unprocessed wheat bran to the cereal.
Add Whole Grains - Try to make at least half of the grains eaten whole grains.
- Look for bread that lists whole wheat, whole-wheat flour, or another whole grain as the first ingredient, with at least 2 grams of dietary fiber per serving.
- Experiment with whole-wheat pasta, brown rice, wild rice, barley, and bulgur wheat.
Baked Foods - Substitute whole-grain flour for half or all white flour when baking.
- Add crushed bran cereal, unprocessed wheat bran, or uncooked oatmeal to muffins, cakes, and cookies.
Legumes - Beans, peas, and lentils are recommended sources.
- Add kidney beans to soups or salads.
- Make nachos with refried black beans, fresh vegetables, whole-wheat tortilla chips, and healthy salsa.
Fruit and Vegetables - Fruits and vegetables are rich in fiber and vitamins and minerals.
- Try to eat a favorite fruit daily.
Healthy Snacks - Fresh fruits, raw vegetables, low-fat popcorn, and whole-grain crackers are healthy choices.
- Try for a handful of nuts or dried fruits; however, be aware that nuts and dried fruits can be high in calories.
Moderation High-fiber foods are beneficial for the body's health. - Adding too much fiber can promote intestinal gas, abdominal bloating, and cramping.
- Increase fiber gradually over a few weeks.
- This allows the natural bacteria in the digestive system to make adjustments.
- Maintain hydration, as fiber works best when it absorbs water.
Individuals not sure how to incorporate more fiber can consult a nutritionist and health coach to help begin the process. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Anderson, James W et al. "Health benefits of dietary fiber." Nutrition Reviews vol. 67,4 (2009): 188-205. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2009.00189.x Cronin, Peter, et al. "Dietary Fiber Modulates the Gut Microbiota." Nutrients vol. 13,5 1655. 13 May. 2021, doi:10.3390/nu13051655 Fuller, Stacey, et al. "New Horizons for the Study of Dietary Fiber and Health: A Review." Plant foods for human nutrition (Dordrecht, Netherlands) vol. 71,1 (2016): 1-12. doi:10.1007/s11130-016-0529-6 Gill, Samantha K et al. "Dietary fiber in gastrointestinal health and disease." Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology vol. 18,2 (2021): 101-116. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-00375-4
The central nervous system - CNS controls body and mind functions, voluntary movements, including walking, and involuntary movements, specifically the breakdown of foods and waste removal. Studies have found associations between spinal problems and gastrointestinal-GI tract/stomach issues that include: - Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Difficulty controlling bowel movements
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Treating the underlying cause through chiropractic, non-surgical spinal decompression, and health coaching can bring pain relief, realign/heal the spine and alleviate stomach issues. Spinal Problems and Stomach Issues The spinal cord sends nerve signals throughout the body, including to and from the digestive system. Two types of nerves control the digestive system, extrinsic and intrinsic. Extrinsic nerves - Connect the digestive organs with the brain and spinal cord.
- Release chemicals that contract or relax the digestive system muscles.
Intrinsic nerves - Are a sub-nervous system of the intestinal tract.
- The nerves activate when the walls of the intestines become filled with food.
- They control the production of digestive juices.
- The nerves relay signals to speed up or slow down the food’s movement through the gut.
The intrinsic system can function independently and work without communication from the extrinsic nerves. However, the stomach and esophagus/food pipe depends on information from the extrinsic nerves. If there is injury, damage, or interference with the extrinsic nerve supply to the stomach, it can lead to stomach issues. Spinal cord injuries and compressed or herniated discs interrupt the communication between nerves/systems, which can lead to digestive and bowel problems, including: - Feeling full quickly after eating.
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Decreased appetite
- Difficulty moving waste through the colon or large intestine
- Hard stools
- Tenesmus - the sensation/feeling of having to have a bowel movement even though there is none.
Herniated Discs Herniated disc/s usually occurs in the neck or low back spinal area. Symptoms include: - Neck pain
- Back pain
- Pain spreads from the lower back through the buttocks, legs, and feet.
- Pain spreads from the neck through the shoulders, arms, and hands.
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle spasms
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Numbness
Chiropractic Spinal Decompression Chiropractic decompression therapy stretches the spine and manipulates its position to take pressure off the nerves and spinal discs. The decompression process creates negative pressure in the discs that retract herniated or bulging discs, allowing oxygen, water, and other healing nutrients to enter the disc and throughout the spine. The spinal decompression will help alleviate the stomach issues. Consultation from a health coach/nutritionist will recommend a diet that will aid in the disc/s healing, which is anti-inflammatory and easily digestible until the stomach problems are fully resolved. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Browning, Kirsteen N, and R Alberto Travagli. “Central nervous system control of gastrointestinal motility and secretion and modulation of gastrointestinal functions.” Comprehensive Physiology vol. 4,4 (2014): 1339-68. doi:10.1002/cphy.c130055 Holmes, Gregory M, and Emily N Blanke. “Gastrointestinal dysfunction after spinal cord injury.” Experimental neurology vol. 320 (2019): 113009. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113009 Lara, F J Pérez, et al. “Thoracic disk herniation, a not infrequent cause of chronic abdominal pain.” International surgery vol. 97,1 (2012): 27-33. doi:10.9738/CC98.1 Papadakos, Nikolaos, et al. “Thoracic disc prolapse presenting with abdominal pain: case report and review of the literature.” Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England vol. 91,5 (2009): W4-6. doi:10.1308/147870809X401038
|
For individuals dealing with ulcerative colitis, can acupuncture treatment benefit those with UC and other GI-related issues? Acupuncture For Ulcerative Colitis Acupuncture has been used to treat symptoms related to pain and inflammation. Studies suggest it may help reduce inflammation and symptoms like diarrhea and abdominal pain, which could benefit individuals with inflammatory bowel disease. Individuals with ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease/IBD affecting the large intestine, may find acupuncture beneficial in managing symptoms, including pain and gastrointestinal symptoms. (Crohn's and Colitis Foundation, 2019) - There are 2,000 acupoints in the body connected by pathways known as meridians. (Wilkinson J, Faleiro R. 2007)
- The pathways connecting the acupoints generate energy, which contributes to overall health.
- A disruption to the energy flow can cause injury, illness, or disease.
- When acupuncture needles are inserted, energy flow and health are improved.
Benefits Acupuncture can be used for the relief of various conditions. Studies have shown that acupuncture can reduce inflammation and disease activity in individuals with an IBD, like UC and Crohn's disease. It can help with: (Gengqing Song et al., 2019) - Pain symptoms
- Gut microbiome imbalances
- Gut motor dysfunction
- Intestinal barrier function
- Anxiety
- Depression
Studies suggest the use of acupuncture with heat, known as moxibustion, can improve several GI symptoms including (Crohn's and Colitis Foundation, 2019) - Bloating
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Gas
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
It is effective in the treatment of digestive issues that include: (Johns Hopkins Medicine. 2024) - Gastritis
- Irritable bowel syndrome/IBS
- Hemorrhoids
- Hepatitis
Reduces Pain and Inflammation - Acupuncture treatment works by releasing endorphins, which help reduce pain. (Harvard Medical School. 2016)
- Applying pressure to acupoints triggers the central nervous system.
- This is believed to cause the release of chemicals that stimulate the body's healing mechanisms. (Johns Hopkins Medicine. 2024)
- Studies have also found acupuncture can trigger the production of cortisol.
- This hormone helps control inflammation. (Arthritis Foundation. N.D.)
- Studies found the use of acupuncture along with moxibustion reduced inflammation in individuals with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. (Crohn's and Colitis Foundation, 2019)
Stress and Mood Chronic conditions like ulcerative colitis can cause feelings of depression and/or anxiety. Acupuncture may be used to address symptoms related to stress and mood and can benefit emotional health issues that include: (Johns Hopkins Medicine. 2024) - Insomnia
- Anxiety
- Nervousness
- Depression
- Neurosis - mental health condition characterized by chronic distress and anxiety.
Side Effects Acupuncture is considered a safe practice. The most common side effects are: (GI Society. 2024) - Bruising
- Minor bleeding
- Increased pain
- Fainting can occur due to needle shock.
- Needle shock can cause dizziness, feeling faint, and nausea. (Harvard Medical School. 2023)
- Needle shock is rare but more common in individuals:
- Who are regularly nervous.
- Who are nervous around needles.
- Who are new to acupuncture.
- Who have a history of fainting.
- Who are extremely fatigued.
- Who have low blood sugar.
For some, GI symptoms may worsen before they improve. It is recommended to try at least five sessions as this is part of the healing process. (Cleveland Clinic. 2023) However, individuals should contact their doctor if symptoms become severe or last more than two days. (GI Society. 2024) Individuals considering acupuncture to help manage symptoms of ulcerative colitis should speak with their healthcare provider to help determine the appropriate treatment and where to start. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Crohn's and Colitis Foundation. (2019). Acupuncture in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. IBDVisible Blog. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/blog/acupuncture-inflammatory-bowel-disease Wilkinson J, Faleiro R. (2007). Acupuncture in pain management. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care and Pain. 7(4), 135-138. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkm021 Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2024). Acupuncture (Health, Issue. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/acupuncture Song, G., Fiocchi, C., & Achkar, J. P. (2019). Acupuncture in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammatory bowel diseases, 25(7), 1129–1139. https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izy371 Harvard Medical School. (2016). Relieving pain with acupuncture. Harvard Health Blog. https://www.health.harvard.edu/healthbeat/relieving-pain-with-acupuncture Arthritis Foundation. (N.D.). Acupuncture for Arthritis. Health Wellness. https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/treatment/complementary-therapies/natural-therapies/acupuncture-for-arthritis Harvard Medical School. (2023). Acupuncture: what is it? Harvard Health Publishing Harvard Medical School Blog. https://www.health.harvard.edu/a_to_z/acupuncture-a-to-z#:~:text=The%20most%20common%20side%20effects,injury%20to%20an%20internal%20organ. Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Acupuncture. Health Library. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/4767-acupuncture GI Society. (2024). Acupuncture and Digestion. badgut.org. https://badgut.org/information-centre/a-z-digestive-topics/acupuncture-and-digestion/
For individuals with digestive and other health issues, could resistant starch provide health benefits? Resistant Starch Typical starchy foods are simple starches that are rapidly digested. This sends their sugars into the bloodstream, contributing to weight gain and increasing the risk of diabetes and heart disease. (Erik E. J. G. Aller, et al., 2011) Resistant starch is a food component that is a type resistant to digestion. This means that it passes into the large intestine and interacts with the gut flora. Foods that contain resistant starch pass through the stomach and small intestine without being absorbed. In the large intestine, they are fermented by the gut bacteria which releases substances that are beneficial to health. Health Benefits Studies on the health benefits are ongoing. Scientists are researching how it can help with weight management and colon health: Weight Management Research is beginning to show indications that foods with resistant starch can help with weight loss and the ability to help offset the diseases associated with weight gain that include: (Janine A. Higgins. 2014) - High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Cardiovascular disease
Colon Health In addition, researchers are finding preliminary evidence indicating that resistant starch might possibly help with: (Diane F. Birt, et al., 2013) - A prebiotic that encourages a healthy balance of gut flora.
- Inflammatory bowel disease symptom improvement.
- Prevention of colon cancer.
- Protection against diverticulitis.
However, more research is needed. Consumption Amount Estimates on how much should be consumed range from a minimum of 6 grams to a maximum of 30 grams. It is estimated that most individuals consume less than 5 grams per day, (Mary M. Murphy, et al., 2008). As individuals increase their intake, it is recommended to do so slowly, to minimize unwanted gas and bloating. Bananas - Bananas are a healthy source of resistant starch.
- They have the maximum amount when they are unripe.
- The resistant starch content reduces as the banana ripens.
- If green/unripe bananas are not appealing, making a smoothie can help with the taste.
Potatoes - Potatoes have their highest level of resistant starch when raw.
- However, individuals can maximize their intake by allowing the potatoes to cool before eating.
Rice - Levels of resistant starch depend on whether the rice is white or brown.
- Similar to potatoes, intake can be maximized from rice by allowing the rice to cool.
Oats - Cooking oats in water, as most are accustomed to making oatmeal, diminishes the resistant starch content.
- Rolled or steel-cut oats are recommended as dependable sources of resistant starch.
Chickpeas - Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are nutritional powerhouses.
- They are a healthy source of dietary fiber, along with many vitamins and minerals, and resistant starch.
- Cooked and/or canned chickpeas contain high levels of resistant starch.
- They go with salads or as a side dish or snack.
- For individuals with IBS, well-rinsed canned chickpeas are considered to be low in FODMAPs or carbohydrates that can contribute to symptoms. (Anamaria Cozma-Petruţ, et al., 2017)
- It is recommended to keep the serving size to a 1/4 cup.
Lentils - Lentils serve as a healthy source of plant-based protein.
- Cooked they can provide resistant starch.
- They can be prepared in soups or side dishes.
- From a can, they can be IBS-friendly by being well-rinsed and limited to a 1/2 cup serving.
Bread - Various breads offer varying levels of resistant starch.
- Pumpernickel bread contains high levels.
- Breadsticks and pizza crusts have high levels.
- Individuals with IBS may be reactive to the FODMAP fructan or the gluten protein.
- Other recommended high-resistant starch options are corn tortillas or artisanal sourdough bread that is traditionally prepared.
Green Peas - Green peas, even when cooked, are a healthy source of resistant starch.
- They can be prepared in soups or as a side dish.
- However, green peas have been found to be high in the FODMAP GOS and could be problematic for individuals with IBS. (Anamaria Cozma-Petruţ, et al., 2017)
Beans - Most types of cooked and/or canned beans are recommended sources of resistant starch.
- The highest levels are found in white and kidney beans.
- They can be served in soups, as a side dish, or mixed with rice.
- Beans are a high-FODMAP food and could contribute to digestive symptoms in individuals with IBS.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Aller, E. E., Abete, I., Astrup, A., Martinez, J. A., & van Baak, M. A. (2011). Starches, sugars and obesity. Nutrients, 3(3), 341–369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3030341 Higgins J. A. (2014). Resistant starch and energy balance: impact on weight loss and maintenance. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 54(9), 1158–1166. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2011.629352 Birt, D. F., Boylston, T., Hendrich, S., Jane, J. L., Hollis, J., Li, L., McClelland, J., Moore, S., Phillips, G. J., Rowling, M., Schalinske, K., Scott, M. P., & Whitley, E. M. (2013). Resistant starch: promise for improving human health. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 4(6), 587–601. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.113.004325 Murphy, M. M., Douglass, J. S., & Birkett, A. (2008). Resistant starch intakes in the United States. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 108(1), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2007.10.012 Cozma-Petruţ, A., Loghin, F., Miere, D., & Dumitraşcu, D. L. (2017). Diet in irritable bowel syndrome: What to recommend, not what to forbid to patients!. World journal of gastroenterology, 23(21), 3771–3783. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3771
For individuals with stomach issues, can maintaining gut flora balance promote and improve gut health? Gut Flora Balance Maintaining gut flora balance is part of optimal digestive health. Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tract. The type and amount of bacteria present depend on their location in the body which could be the small intestine and colon. This is the storage housing for waste/stool, and the colon comprises hundreds of different types of bacteria, which have specific jobs and functions. Unhealthy Flora The more common pathogens are bacteria that can cause illness if left unchecked, including germs like streptococcus/strep throat or E. coli/urinary tract infections and diarrhea. Other common germs found in the colon include: (Elizabeth Thursby, Nathalie Juge. 2017) Clostridioides Difficile - C. diff overgrowth can cause watery foul-smelling stools daily, and abdominal pain and tenderness.
Enterococcus Faecalis - Enterococcus faecalis is a cause of post-surgical abdominal and urinary tract infections.
Escherichia Coli - E. coli is the most common cause of diarrhea in adults.
- This bacteria is present in almost every healthy adult’s colon.
Klebsiella - Klebsiella overgrowth is associated with a Western diet that consists of various meat and animal products.
Bacteroides - Bacteroide overgrowth is associated with colitis, which causes painful inflammation of the colon.
Healthy Flora Healthy bacteria like Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus, help maintain gut flora balance and keep the unhealthy bacteria in check. Without healthy flora, the entire colon can become overrun by bad flora, which can result in symptoms like diarrhea and/or illness. (Yu-Jie Zhang, et al., 2015) These protective, microscopic germs have important functions that include: - Assisting with vitamin synthesis - vitamins B and K in the small intestine.
- Increases immune system function.
- Maintaining regular bowel movements.
- Maintaining a clean colon naturally without the need for colon cleansers.
- Destroying the unhealthy bacteria.
- Preventing unhealthy bacteria overgrowth.
- Breaking up gas bubbles from food fermentation.
Bacterial Dismantling Whether labeled as healthy bacteria or unhealthy, they are both single-celled organisms that can be destroyed quite easily. Sometimes, it is necessary, like when having to take antibiotics to kill a strep throat infection. However, the antibiotics also kill the beneficial bacteria, which can lead to compounding problems that can include: (Mi Young Yoon, Sang Sun Yoon. 2018) - Bowel irregularity - diarrhea and constipation.
- Yeast overgrowth - can cause itching, burning around the anus and lead to vaginal and oral yeast infections.
- Dysbiosis - the technical name for a lack of healthy bacteria or a bacterial imbalance.
- Complications for individuals suffering from irritable bowel syndrome.
There are different ways to destroy bacteria including. - Individuals who need to take antibiotics to cure an infection. (Eamonn M M Quigley. 2013)
- Chronic laxative use.
- Fiber supplementation overuse.
- Prolonged diarrhea - can flush out the bad and good bacteria.
- Stress
- Completing a bowel prep, like those required for a colonoscopy.
Diagnosing Gut Flora Issues Many times, problems with gut flora will correct themselves, and no action is required. However, individuals facing chronic bowel problems, like colitis or inflammatory bowel disease, may require medical intervention of their colon's bacteria. - Comprehensive Digestive Stool Analysis/CDSA is a stool test that checks what type and amount of bacteria are present, nutrient absorption rates/digestion speed, and how well food is digested.
- If there is a significant difference in the proportion of unhealthy versus beneficial bacteria, a healthcare provider may suggest taking a probiotic or a live microbial supplement to help repopulate and maintain gut flora balance.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Thursby, E., & Juge, N. (2017). Introduction to the human gut microbiota. The Biochemical journal, 474(11), 1823–1836. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160510 Zhang, Y. J., Li, S., Gan, R. Y., Zhou, T., Xu, D. P., & Li, H. B. (2015). Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. International journal of molecular sciences, 16(4), 7493–7519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047493 Yoon, M. Y., & Yoon, S. S. (2018). Disruption of the Gut Ecosystem by Antibiotics. Yonsei medical journal, 59(1), 4–12. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.4 Quigley E. M. (2013). Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterology & hepatology, 9(9), 560–569.
The digestive system breaks down the foods eaten so the body can absorb the nutrients. During digestion, the unnecessary parts of these foods are turned into waste/stool, which is evacuated during a bowel movement. When the digestive system stops functioning properly due to factors such as diet change, eating unhealthy foods, lack of physical activity/exercise, medications, and certain health conditions, can cause constipation. Constipation occurs when the body cannot have a regular bowel movement. The distention, gas, bloating and not being able to have a bowel movement cause irritability and stress, which can worsen constipation. Incorporating recommended nutrition can help restore regular bowel movements and gut function. Recommended Nutrition For Constipation Symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and difficult bowel movements are common. Diet and proper hydration have a significant role in digestive health, especially in relieving and preventing constipation. High-fiber foods, prebiotics, and adequate hydration from foods and beverages are essential for healthy bowel movements. - Fiber is found in whole grains, starches, fruits, and vegetables.
- Soluble and insoluble fiber are important for digestive health.
- Focusing on incorporating high-fiber fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Foods rich in prebiotics like fermented foods are recommended when constipated.
The recommended nutrition for constipation, according to a dietitian includes. Avocados - Avocados can be paired with just about anything and are full of nutrients and fiber.
- One avocado contains around 13.5 grams of fiber.
- One avocado will provide almost half daily fiber needs.
- Other high-fiber fruits: pomegranates, guava, raspberries, blackberries, and passionfruit.
Figs - Figs can be eaten fresh and dried.
- Figs are considered a laxative and have been shown to treat and reduce constipation.
- They contain antioxidants, polyphenols, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and vitamins.
- Other fruits similar to a fig: dried apricots, prunes, and plums.
Plums - Plums, prunes dried plums are packed with fiber and prebiotics that have a natural laxative effect.
- Sorbitol - a sugar found in plums and prunes, acts as an osmotic laxative that retains water.
- The added H2O makes the stools softer and easier to pass.
- Natural fruit juices, like pear, apple, or prune are often prescribed for constipation.
- Other fruits that aid in bowel movements: peaches, pears, and apples.
Kefir - Fermented foods like kefir are rich in beneficial bacteria that work to maintain digestive system health.
- It can be consumed on its own or used in smoothies, cooking, and baking recipes.
- Other fermented foods: kombucha, yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and tempeh.
Oat Bran - Oat bran is oatmeal that has not had the bran removed.
- The bran contains beneficial nutrients including fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
- Oat bran contains soluble and insoluble fiber, as well as beta-glucan/non-starchy polysaccharides.
- All improve the composition of gut bacteria and promote healthy bowel movements.
- Other beneficial grains: oatmeal, wheat bran, rye, and barley.
Incorporating Gut-Beneficial Foods How to incorporate recommended nutrition gut-beneficial foods into a regular menu: Smoothie - Use kefir or yogurt as a base then balance it out with fiber-rich fruits like mango, blueberries, and kiwi.
Snacks - Diversify snacks with a plate of fiber and prebiotics.
- Nuts, cheese, crackers, fruit, and a yogurt or avocado dip.
Oatmeal - Try oat bran to increase fiber.
- Sprinkle a serving of flaxseeds, chia seeds, or hemp seeds for added fiber and healthy fats.
Parfait - Yogurt parfaits can maximize nutrients, flavor, and textures in a bowl.
- Layer up on a favorite yogurt with granola, nuts, fruit, and seeds.
Grain Bowl - Fiber found in whole grains and seeds like barley, farro, and quinoa, helps promote healthy digestion.
- Make a bowl with a grain base, then top with a protein, fresh or grilled veggies, avocado, and dressing.
Talk with a registered nutritionist or other healthcare provider to discuss recommended nutrition plan options. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Arce, Daisy A et al. “Evaluation of constipation.” American family physician vol. 65,11 (2002): 2283-90. Bharucha, Adil E. “Constipation.” Best practice & research. Clinical gastroenterology vol. 21,4 (2007): 709-31. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2007.07.001 Gray, James R. “What is chronic constipation? Definition and diagnosis.” Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology = Journal Canadien de Gastroenterology vol. 25 Suppl B, Suppl B (2011): 7B-10B. Jani, Bhairvi, and Elizabeth Marsicano. “Constipation: Evaluation and Management.” Missouri medicine vol. 115,3 (2018): 236-240. Naseer, Maliha, et al. “Therapeutic Effects of Prebiotics on Constipation: A Schematic Review.” Current clinical pharmacology vol. 15,3 (2020): 207-215. doi:10.2174/1574884715666200212125035 National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Symptoms and Causes of Constipation. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease. Your Digestive System and How It Works. Sinclair, Marybetts. “The use of abdominal massage to treat chronic constipation.” Journal of bodywork and movement therapies vol. 15,4 (2011): 436-45. doi:10.1016/j.jbmt.2010.07.007
Before the body can benefit from consumed nutrients, the gastrointestinal tract has to digest and absorb the foods. Before eating, the body needs to feel hungry. However, hunger is not the same as appetite. Hunger is a physical reaction caused by hormonal and chemical changes in the body when fuel is needed. Appetite is more of a desire to eat and can be a learned response. It is one reason why individuals can eat when they are not hungry. The body comprises different hormones that regulate hunger, digestion, and appetite. Hunger Digestion Regulating Hormones Hunger Hormones Hunger is the feeling when the body needs food. When the body has enough, hunger should subside. That's because various hormones regulate hunger. Leptin - Leptin is a hormone secreted by adipose tissue/fat into the bloodstream.
- The more fat in the body, the higher the blood levels of leptin.
- Leptin level also increases with food intake and is higher in females than males, but overall, it lowers with age.
- Increased leptin levels trigger the hypothalamus to reduce hunger.
Ghrelin - Ghrelin is a hormone produced by the stomach and small intestine when the stomach is empty.
- Like leptin, it also works with the hypothalamus.
- However, instead of suppressing hunger, it increases hunger.
Insulin - The pancreas produces this hormone.
- It is mostly known for regulating blood sugar levels.
- It also suppresses hunger.
Adiponectin - Adiponectin is a hormone secreted by fat cells.
- As body fat levels go down, this hormone goes up.
- If fat levels go up, adiponectin levels go down.
Cholecystokinin - Cholecystokinin is a hormone produced in the small intestine during and after a meal.
- It triggers the release of bile and digestive enzymes into the small intestine.
- These suppress hunger and make the body feel full.
Peptide YY - This hormone suppresses appetite for about 12 hours after eating.
- Made by both the large and small intestines after eating.
Glucocorticoids - Adrenal glands make these hormones, and their primary function is to regulate inflammation and other processes, but they also impact hunger.
- A cortisol deficiency reduces appetite, but excessive amounts of glucocorticoids increase hunger.
Digestion Hormones Digestion is coordinated and regulated by hormones. Gastrin - Gastrin is a hormone the stomach and the small intestine release when eating.
- Gastrin stimulates the release of hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen in the stomach to speed up digestion.
- Gastrin stimulates glucagon, which works with insulin to regulate blood sugar.
Secretin - Secretin is a hormone made by the small intestine.
- It is secreted into the bloodstream when the acidic chyme from the stomach enters the small intestine.
- Secretin stimulates the pancreas to release bicarbonate digestive liquids into the small intestine.
- The bicarbonate neutralizes the acidity.
- Secretin acts on the stomach to trigger the production of pepsinogen to help break down proteins.
Cholecystokinin - CCK - The small intestine makes and releases CCK into the bloodstream.
- Essential fat digestion stimulates the gallbladder to release bile into the small intestine.
- It also triggers the pancreas to release various digestive enzymes so they can break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Motilin - The small intestine makes Motilin.
- Motilin speeds up activity in the stomach and small intestine.
- It also stimulates the stomach and pancreas to release various secretions and causes the gallbladder to contract.
Glucose - Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide - GIP - Sometimes called a gastric inhibitory peptide.
- The small intestine makes this hormone.
- It stimulates the pancreas to release insulin and slows down stomach digestive activity.
Peptide YY and Enterogastrone - Released by the small intestine, two more hormones slow digestion down and decrease the production of digestive secretions.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Chandra, Rashmi, and Rodger A Liddle. "Cholecystokinin." Current Opinion in Endocrinology, diabetes, and Obesity vol. 14,1 (2007): 63-7. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3280122850 Davis, Jon. “Hunger, ghrelin and the gut.” Brain Research vol. 1693, Pt B (2018): 154-158. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2018.01.024 Gupta K, Raja A. Physiology, Gastric Inhibitory Peptide. [Updated 2022 Sep 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546653/ Konturek, S J et al. “Brain-gut axis and its role in the control of food intake.” Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology: an official journal of the Polish Physiological Society vol. 55,1 Pt 2 (2004): 137-54. Prosapio JG, Sankar P, Jialal I. Physiology, Gastrin. [Updated 2023 Apr 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534822/ Rix I, Nexøe-Larsen C, Bergmann NC, et al. Glucagon Physiology. [Updated 2019 Jul 16]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279127/ Suzuki, Keisuke, et al. "The role of gut hormones and the hypothalamus in appetite regulation." Endocrine Journal vol. 57,5 (2010): 359-72. doi:10.1507/endocrine.k10e-077 Tack, Jan, et al. "The gastrointestinal tract in hunger and satiety signaling." United European gastroenterology journal vol. 9,6 (2021): 727-734. doi:10.1002/ueg2.12097 Zanchi, Davide, et al. "The impact of gut hormones on the neural circuit of appetite and satiety: A systematic review." Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews vol. 80 (2017): 457-475. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.06.013
Body misalignment can cause various symptoms to be experienced, ranging from headaches, neck and back pain, sore feet, discomfort in the joints, muscles, or nerves, and digestive problems. Improperly aligned vertebrae can press against nerves, pinching or compressing them, causing the nerve signals of the digestive system, including those in the stomach and intestines, to misfire or fail to transmit at the appropriate moment. This can cause the organs to malfunction, resulting in heartburn, gas, constipation, cramping, diarrhea, and other symptoms. Chiropractic realignment adjustments are an effective treatment option for frequent stomachaches, reflux, constipation, and other gastrointestinal conditions. Body Misalignment Digestive Problems There are over a million nerve cells within the digestive system. A collection of nerves branch out from the lower part of the spinal cord and travels to the stomach and intestines. Nerve transmission plays an essential role in the following: - Digestion.
- Movement of food through the gastrointestinal system.
- Absorption of nutrients and minerals.
- Removal of waste products.
Misalignments of the vertebrae are known as subluxations. Pressure on nerve roots caused by misalignment can interfere with the function of the bowel and other organs, which can lead to gastrointestinal issues. Muscle tension in the abdomen can also contribute to digestive problems, whether because of stress or sitting for long hours daily. Misalignment Symptoms When the body is out of alignment, symptoms of discomfort begin to appear. The most common include: - Fatigue.
- Stiff neck.
- Sore shoulders.
- Chronic headaches.
- Sore muscles.
- Pain throughout the back.
- Joint pain throughout the body.
- Chronic aches.
- Tight hips.
- Difficulty walking.
- Tingling, pins and needles, and numbness nerve sensations - sciatica.
- Constantly getting sick.
Healthy Gut A balanced healthy gut will have less difficulty processing food and eliminating waste, leading to reduced and eventually alleviated symptoms. The following show healthy gut function: - Regular, consistent energy levels.
- Increased mental clarity.
- Regular and healthy bowel movements.
- No pain or discomfort symptoms.
- A normal amount of gas and bloating.
- Healthy stress levels.
Chiropractic Chiropractic care will realign the body to its proper form, improving gastrointestinal issues. The chiropractic team will use various tools and techniques to guide and correct any subluxations, relax the muscles, and increase nerve and blood circulation. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Ernst, Edzard. “Chiropractic treatment for gastrointestinal problems: a systematic review of clinical trials.” Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology = Journal canadien de Gastroenterologie vol. 25,1 (2011): 39-40. doi:10.1155/2011/910469 Hills, Ronald D Jr, et al. “Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease.” Nutrients vol. 11,7 1613. 16 Jul. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11071613 Hornbuckle, William E., et al. “Gastrointestinal Function.” Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals (2008): 413–457. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-370491-7.00014-3 Leeming, Emily R et al. “Effect of Diet on the Gut Microbiota: Rethinking Intervention Duration.” Nutrients vol. 11,12 2862. 22 Nov. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11122862 Li, Yuanyuan, et al. “The Role of Microbiome in Insomnia, Circadian Disturbance, and Depression.” Frontiers in psychiatry vol. 9 669. 5 Dec. 2018, doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00669 Redwood, Daniel. “Chiropractic and visceral disorders.” Journal of Alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.) vol. 13,5 (2007): 479-80. doi:10.1089/acm.2007.7146 Valdes, Ana M et al. “Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health.” BMJ (Clinical research ed.) vol. 361 k2179. 13 Jun. 2018, doi:10.1136/bmj.k2179
Spinal decompression and Digestion. No one wants to worry about stomach issues. A rich and unhealthy diet can cause digestive issues, stomach pain, and back pain. This can turn into a severe chronic condition; studies have found links between spinal problems and gastrointestinal tract symptoms, which include: - Abdominal pain that radiates.
- Constipation.
- Difficulty controlling bowel movements.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
Chiropractic treats the spine that is essential to the function of the central nervous system, which is responsible for digestion. When the nervous system is not functioning correctly, the other systems begin to malfunction. Chiropractic manual and motorized spinal decompression can help with digestion by releasing trapped gas from joints while improving blood circulation that is natural and non-invasive. Spinal Decompression and Digestion Spinal alignment and digestion are closely connected. The nerves in the thoracic and lumbar regions affect digestion. When the spine is out of alignment, it stresses the nerves. Nerves that are pinched or constricted are inhibited/disrupted from sending the proper signals to the digestive system. This can lead to new or worsening digestive problems. Spinal conditions that can cause digestive issues: - Herniated discs
- Ankylosing spondylosis
- Spinal cord injuries
- Tumors
Studies have found that digestive issues, including discomfort, heartburn, and bloating, have decreased with regular chiropractic and spinal decompression and decreased constipation and irregular bowel movements. This comes from chiropractic reactivating the body’s natural ability to heal itself. Increased Circulation - When the spine gets decompressed, it opens up the spine to circulate fluids throughout the body.
- This flushes the lymphatic system, increasing the immune system's function.
- Increasing the circulation also provides additional oxygen and nutrients to the brain, improving signaling, memory, and concentration.
Improved Digestion - Poor posture compresses the abdomen and cramps the space the gastrointestinal tract needs to process food properly.
- Decompressing the spine and correcting posture allows room for the muscles to contract, expand, and properly circulate waste.
Bowel Program Treatment focuses on preventing further injuries and helping improve the individual's quality of life. A doctor, chiropractor, health coach, or nutritionist can recommend a bowel program to help retrain the body to maintain regular bowel movements. These programs are personalized to the individual's specific condition that takes into account: - Level of the spine injury or condition
- Food and drink intake
- Bowel movement pattern
- Digestive problems
- General health
- Individual preferences
A bowel program sets up the timing of food intake, fluid intake, medications, and techniques to help bowel movements. The objective is to prevent spontaneous bowel movements, help pass stools regularly, and empty the rectum daily. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Browning, Kirsteen N, and R Alberto Travagli. “Central nervous system control of gastrointestinal motility and secretion and modulation of gastrointestinal functions.” Comprehensive Physiology vol. 4,4 (2014): 1339-68. doi:10.1002/cphy.c130055 Holmes, Gregory M, and Emily N Blanke. “Gastrointestinal dysfunction after spinal cord injury.” Experimental neurology vol. 320 (2019): 113009. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113009 Kehl, Amy S et al. “Relationship between the gut and the spine: a pilot study of first-degree relatives of patients with ankylosing spondylitis.” RMD open vol. 3,2 e000437. 16 Aug. 2017, doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000437 Lara, Francisco Javier Pérez et al. “Chronic abdominal syndrome due to nervous compression. Study of 100 cases and proposed diagnostic-therapeutic algorithm.” Journal of gastrointestinal surgery: official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract vol. 19,6 (2015): 1059-71. doi:10.1007/s11605-015-2801-8
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...









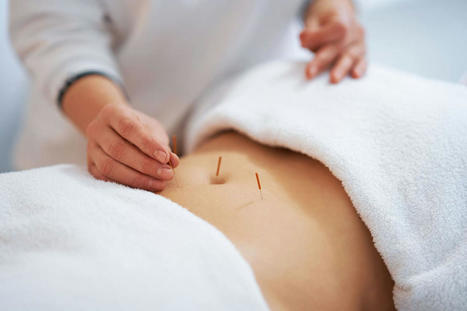










Walking for constipation relief: learn how this simple exercise can help regulate bowel movements and improve quality of life. For answers to any questions you may have, call Dr. Alexander Jimenez at 915-850-0900 or 915-412-6677