 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Can knowing which foods to eat help individuals recovering from food poisoning restore gut health? Food Poisoning and Restoring Gut Health Food poisoning can be life-threatening. Fortunately, most cases are mild and short-lived and last only a few hours to a few days (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024). But even mild cases can wreak havoc on the gut, causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Researchers have found that bacterial infections, like food poisoning, can cause changes in gut bacteria. (Clara Belzer et al., 2014) Eating foods that promote gut healing after food poisoning may help the body recover and feel better faster. Foods to Eat After food poisoning symptoms have resolved, one may feel that returning to the usual diet is fine. However, the gut has endured quite an experience, and even though acute symptoms have subsided, individuals may still benefit from foods and drinks that are easier on the stomach. Recommended foods and beverages after food poisoning include: (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2019) - Gatorade
- Pedialyte
- Water
- Herbal tea
- Chicken broth
- Jello
- Applesauce
- Crackers
- Toast
- Rice
- Oatmeal
- Bananas
- Potatoes
Hydration after food poisoning is crucial. Individuals should add other nutritious and hydrating foods, like chicken noodle soup, which helps because of its nutrients and fluid content. The diarrhea and vomiting that accompany the illness can leave the body severely dehydrated. Rehydrating beverages help the body replace lost electrolytes and sodium. Once the body is rehydrated and can hold down bland foods, slowly introduce foods from a regular diet. When resuming the usual diet after rehydration, eating small meals frequently, every three to four hours, is recommended instead of eating a large breakfast, lunch, and dinner meal daily. (Andi L. Shane et al., 2017) When choosing Gatorade or Pedialyte, remember that Gatorade is a sports-rehydrating drink with more sugar, which could irritate an inflamed stomach. Pedialyte is designed for rehydrating during and after illness and has less sugar, making it a better option. (Ronald J Maughan et al., 2016) When Food Poisoning Is Active Foods To Avoid During food poisoning, individuals typically do not feel like eating at all. However, to avoid worsening the illness, Individuals are recommended to avoid the following while actively ill (Ohio State University. 2019) - Caffeinated drinks and alcohol can further dehydrate.
- Greasy foods and high-fiber foods are hard to digest.
- Foods and beverages high in sugar can cause the body to produce high glucose levels and weaken the immune system. (Navid Shomali et al., 2021)
Recovery Time and Resuming Regular Diet Food poisoning doesn't last long, and most uncomplicated cases are resolved within a few hours or days. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024) Symptoms depend on the type of bacteria. Individuals may become ill within minutes of consuming contaminated food up to two weeks later. For example, Staphylococcus aureus bacteria generally cause symptoms almost immediately. On the other hand, listeria may take up to a couple of weeks to cause symptoms. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024) Individuals can resume their usual diet once symptoms are gone, the body is thoroughly hydrated and can hold down bland foods. (Andi L. Shane et al., 2017) Recommended Gut Foods Post Stomach Virus Gut-healthy foods can help restore the gut microbiome or all the living microorganisms in the digestive system. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for immune system functioning. (Emanuele Rinninella et al., 2019) Stomach viruses can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. (Chanel A. Mosby et al., 2022) Eating certain foods may help restore the gut balance. Prebiotics, or indigestible plant fibers, can help break down in the small intestines and allow the beneficial bacteria to grow. Prebiotic foods include: (Dorna Davani-Davari et al., 2019) - Beans
- Onions
- Tomatoes
- Asparagus
- Peas
- Honey
- Milk
- Banana
- Wheat, barley, rye
- Garlic
- Soybean
- Seaweed
In addition, probiotics, which are live bacteria, may help increase the number of healthy bacteria in the gut. Probiotic foods include: (Harvard Medical School, 2023) - Pickles
- Sourdough bread
- Kombucha
- Sauerkraut
- Yogurt
- Miso
- Kefir
- Kimchi
- Tempeh
Probiotics can also be taken as a supplement and come in tablets, capsules, powders, and liquids. Because they contain live bacteria, they need to be refrigerated. Healthcare providers sometimes recommend taking probiotics when recovering from a stomach infection. (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2018) Individuals should consult their healthcare provider to see whether this option is safe and healthy. At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we treat injuries and chronic pain syndromes by developing personalized treatment plans and specialized clinical services focused on injuries and the complete recovery process. If other treatment is needed, individuals will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited to their injury, condition, and/or ailment. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Food poisoning symptoms. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/symptoms.html Belzer, C., Gerber, G. K., Roeselers, G., Delaney, M., DuBois, A., Liu, Q., Belavusava, V., Yeliseyev, V., Houseman, A., Onderdonk, A., Cavanaugh, C., & Bry, L. (2014). Dynamics of the microbiota in response to host infection. PloS one, 9(7), e95534. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095534 National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2019). Eating, diet, & nutrition for food poisoning. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/food-poisoning/eating-diet-nutrition Shane, A. L., Mody, R. K., Crump, J. A., Tarr, P. I., Steiner, T. S., Kotloff, K., Langley, J. M., Wanke, C., Warren, C. A., Cheng, A. C., Cantey, J., & Pickering, L. K. (2017). 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Infectious Diarrhea. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 65(12), e45–e80. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cix669 Maughan, R. J., Watson, P., Cordery, P. A., Walsh, N. P., Oliver, S. J., Dolci, A., Rodriguez-Sanchez, N., & Galloway, S. D. (2016). A randomized trial to assess the potential of different beverages to affect hydration status: development of a beverage hydration index. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 103(3), 717–723. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.114769 Ohio State University. Kacie Vavrek, M., RD, CSSD Ohio State University. (2019). Foods to avoid when you have the flu. https://health.osu.edu/wellness/exercise-and-nutrition/foods-to-avoid-with-flu Shomali, N., Mahmoudi, J., Mahmoodpoor, A., Zamiri, R. E., Akbari, M., Xu, H., & Shotorbani, S. S. (2021). Harmful effects of high amounts of glucose on the immune system: An updated review. Biotechnology and applied biochemistry, 68(2), 404–410. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1938 Rinninella, E., Raoul, P., Cintoni, M., Franceschi, F., Miggiano, G. A. D., Gasbarrini, A., & Mele, M. C. (2019). What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms, 7(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7010014 Mosby, C. A., Bhar, S., Phillips, M. B., Edelmann, M. J., & Jones, M. K. (2022). Interaction with mammalian enteric viruses alters outer membrane vesicle production and content by commensal bacteria. Journal of extracellular vesicles, 11(1), e12172. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12172 Davani-Davari, D., Negahdaripour, M., Karimzadeh, I., Seifan, M., Mohkam, M., Masoumi, S. J., Berenjian, A., & Ghasemi, Y. (2019). Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 8(3), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8030092 Harvard Medical School. (2023). How to get more probiotics. https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/how-to-get-more-probiotics National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2018). Treatment of viral gastroenteritis. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/viral-gastroenteritis/treatment
Individuals need to eat more fiber for optimal gut health. Can adding avocado to their diet help improve the gut microbe diversity? Avocado Gut Support A diverse gut microbiome is beneficial to overall health. According to a recent study, eating one avocado a day can help maintain the gut microbes healthy, diverse, and balanced. (Sharon V. Thompson, et al., 2021) The researchers observed positive changes in gut bacteria and increased bacterial diversity in individuals who consumed an avocado every day for 12 weeks. (Susanne M Henning, et al., 2019) Gut Diversity The gut microbiome refers to the microorganisms living in the intestines. There are around 100 trillion microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and more, exist in the gastrointestinal tract. (Ana M. Valdes, et al., 2018) Having a diverse microbiome means that the body has a range of different organisms that offer various health benefits. Not having enough bacterial diversity has been linked to: (Ana M. Valdes, et al., 2018) - Arthritis
- Obesity
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Celiac disease
- Arterial stiffness
- Atopic eczema
Why Avocados? - The Institute of Medicine recommends a daily fiber intake ranging from 19 grams to 38 grams per day, depending on various factors like age. (Diane Quagliani, Patricia Felt-Gunderson. 2016)
- Approximately 95% of adults and children do not consume the recommended amount of fiber. (Diane Quagliani, Patricia Felt-Gunderson. 2016)
- Including foods like avocados in a healthy diet can help meet daily fiber requirements.
- Fruit fiber like pectin, has been shown to promote a healthy gut microbiome as well. (Beukema M, et al., 2020)
- Researchers suggest this could be because of pectin's positive effect on beneficial probiotics.(Nadja Larsen, et al., 2018)
- Although further research is needed fiber is believed to help protect the lining of the colon by increasing the bulk and weight of stool and expediting elimination.
- Fiber also adds bulk to an individual's diet and slows the speed of digestion, which makes the body feel fuller longer.
Improved Gut Individuals can support a healthy microbiota by making small adjustments in their diet, including: - Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables with the skin, as this is where a majority of the nutrition is.
- Fermented foods like yogurt, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kefir.
- Limiting consumption of processed foods, sugar, and artificial sweeteners.
- More whole-grain foods.
Ways to eat more avocados include adding them to: - Smoothies
- Salads
- Sandwichs
- Guacamole
- If there are more avocados that can be eaten before they overripen, they can be frozen.
- Peel and slice them first, then place them in freezer bags to have year-round.
- They are rich in healthy fat, however, in moderation, they are not likely to contribute to weight gain.
Individuals can work toward having a diverse gut microbiome by paying attention to the foods they eat. Specific foods and dietary patterns can influence the different types of bacterial diversity which can support health. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Thompson, S. V., Bailey, M. A., Taylor, A. M., Kaczmarek, J. L., Mysonhimer, A. R., Edwards, C. G., Reeser, G. E., Burd, N. A., Khan, N. A., & Holscher, H. D. (2021). Avocado Consumption Alters Gastrointestinal Bacteria Abundance and Microbial Metabolite Concentrations among Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. The Journal of nutrition, 151(4), 753–762. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxaa219 Henning, S. M., Yang, J., Woo, S. L., Lee, R. P., Huang, J., Rasmusen, A., Carpenter, C. L., Thames, G., Gilbuena, I., Tseng, C. H., Heber, D., & Li, Z. (2019). Hass Avocado Inclusion in a Weight-Loss Diet Supported Weight Loss and Altered Gut Microbiota: A 12-Week Randomized, Parallel-Controlled Trial. Current developments in nutrition, 3(8), nzz068. https://doi.org/10.1093/cdn/nzz068 Valdes, A. M., Walter, J., Segal, E., & Spector, T. D. (2018). Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 361, k2179. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2179 Quagliani, D., & Felt-Gunderson, P. (2016). Closing America's Fiber Intake Gap: Communication Strategies From a Food and Fiber Summit. American journal of lifestyle medicine, 11(1), 80–85. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827615588079 Beukema, M., Faas, M. M., & de Vos, P. (2020). The effects of different dietary fiber pectin structures on the gastrointestinal immune barrier: impact via gut microbiota and direct effects on immune cells. Experimental & molecular medicine, 52(9), 1364–1376. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0449-2 Larsen, N., Cahú, T. B., Isay Saad, S. M., Blennow, A., & Jespersen, L. (2018). The effect of pectins on survival of probiotic Lactobacillus spp. in gastrointestinal juices is related to their structure and physical properties. Food microbiology, 74, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2018.02.015
|
Can incorporating nopal or prickly pear cactus into one's diet help individuals trying to lower blood glucose, inflammation, and risk factors associated with heart and metabolic diseases? Nopal Nopal, also known as prickly pear cactus, is a versatile vegetable that can be added to nutrition plans to increase fiber intake, vitamins, minerals, and plant-based compounds. It grows in the U.S. Southwest, Latin America, and the Mediterranean. The pads, or the nopales or cactus paddles, have a texture like okra and slight tartness. The prickly pear cactus fruit, referred to as tuna in Spanish, is also consumed. (University of Arizona Cooperative Extension, 2019) It is often used in fruit salsas, salads, and desserts and is available as a supplement in tablet and powder form. Serving Size and Nutrition One cup of cooked nopales, around five pads, without added salt, contains: (U.S. Department of Agriculture, FoodData Central, 2018) - Calories - 22
- Fat - 0 grams
- Sodium - 30 milligrams
- Carbohydrates - 5 grams
- Fiber - 3 grams
- Sugars - 1.7 grams
- Protein - 2 grams
- Vitamin A - 600 international units
- Vitamin C - 8 milligrams
- Vitamin K - 8 micrograms
- Potassium - 291 milligrams
- Choline - 11 milligrams
- Calcium - 244 milligrams
- Magnesium - 70 milligrams
It is generally recommended that most individuals consume 2.5 to 4 cups of vegetables per day. (U.S. Department of Agriculture, MyPlate, 2020) Benefits Nopal is highly nutritious, low in calories, free of fat, sodium, or cholesterol, and full of fiber, vitamins, minerals, and betalains. (Parisa Rahimi et al., 2019) Betalains are pigments with anti-inflammatory properties. The variety of fibers creates a low glycemic index (measures how much a specific food raises blood sugar levels after consumption) of about 32, a recommended addition to a diabetes-friendly diet. (Patricia López-Romero et al., 2014) Compounds - Nopal contains a variety of beneficial carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
- Nopal has soluble and insoluble fiber, which benefits blood sugar.
- It also contains vitamin A, carotenoids, vitamin C, calcium, and plant-based compounds like phenols and betalains. (Karina Corona-Cervantes et al., 2022)
Blood Sugar Regulation Research has evaluated regular nopal consumption and supplementation for blood sugar control. A study on blood sugar evaluated adding nopal to a high-carbohydrate breakfast or a breakfast high in soy protein in Mexican individuals with type 2 diabetes. The study found that consuming nopales, about 300 grams or 1.75 to 2 cups before a meal, could reduce after-meal/postprandial blood sugars. (Patricia López-Romero et al., 2014) An older study had similar results. (Montserrat Bacardi-Gascon et al., 2007) Individuals were randomly assigned to consume 85 grams of nopal with three different breakfast options: - Chilaquiles - a casserole made with corn tortilla, vegetable oil, and pinto beans.
- Burritos - made with eggs, vegetable oil, and pinto beans.
- Quesadillas - made with flour tortillas, low-fat cheese, avocado, and pinto beans.
- The groups assigned to eat nopales had reductions in blood sugar. There was a:
- 30% reduction in the chilaquiles group.
- 20% decrease in the burrito group.
- 48% reduction in the quesadilla group.
However, the studies were small, and the population was not diverse. so further research is needed. Increased Fiber The combination of soluble and insoluble fiber benefits the gut in various ways. Soluble fiber can act as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial bacteria in the gut and assisting in removing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol from the body. Insoluble fiber increases transit time, or how quickly food moves through the digestive system and promotes bowel regularity. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022) In a short-term randomized clinical control trial, researchers found an improvement in irritable bowel syndrome symptoms in individuals supplemented with 20 and 30 grams of nopal fiber. (Jose M Remes-Troche et al., 2021) For individuals not used to consuming fibrous foods, it may cause mild diarrhea, so it is recommended to increase intake slowly and with adequate water to prevent gas and bloating. Plant Based Calcium One cup of nopal provides 244 milligrams or 24% of daily calcium needs. Calcium is a mineral that optimizes bone and teeth health. It also assists in blood vessel contraction and dilation, muscle function, blood clotting, nerve transmission, and hormonal secretion. (National Institutes of Health. Office of Dietary Supplements 2024) Individuals who follow diets that exclude dairy products can benefit from plant-based calcium sources. This includes cruciferous vegetables like kale, collards, and arugula. Other Benefits Studies done in animals and test tubes suggest that fresh nopal and extracts may assist in reducing triglycerides and cholesterol in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease or when unhealthy amounts of fat accumulate in the liver. (Karym El-Mostafa et al., 2014) Other potential benefits with limited evidence include: Consult a Dietician or Healthcare Provider Unless individuals are allergic to it, most can eat whole nopal without a problem. However, supplementing is different because it provides a concentrated source. Individuals taking medication to manage diabetes and consuming nopal regularly may contribute to an increased risk of developing hypoglycemia or low blood sugar. Dermatitis has also been reported from contact with the cactus spines. (U.S. Department of Agriculture, FoodData Central, 2018) There have been rare reports of bowel obstruction in individuals who consume large amounts of the seeds found in the fruit. (Karym El-Mostafa et al., 2014) Ask a registered dietitian or primary healthcare provider if nopal can provide safe benefits. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References University of Arizona Cooperative Extension. Hope Wilson, M. W., Patricia Zilliox. (2019). Prickly pear cactus: food of the desert. https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1800-2019.pdf U.S. Department of Agriculture. FoodData Central. (2018). Nopales, cooked, without salt. Retrieved from https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169388/nutrients U.S. Department of Agriculture. MyPlate. (2020-2025). Vegetables. Retrieved from https://www.myplate.gov/eat-healthy/vegetables Rahimi, P., Abedimanesh, S., Mesbah-Namin, S. A., & Ostadrahimi, A. (2019). Betalains, the nature-inspired pigments, in health and diseases. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 59(18), 2949–2978. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1479830 López-Romero, P., Pichardo-Ontiveros, E., Avila-Nava, A., Vázquez-Manjarrez, N., Tovar, A. R., Pedraza-Chaverri, J., & Torres, N. (2014). The effect of nopal (Opuntia ficus indica) on postprandial blood glucose, incretins, and antioxidant activity in Mexican patients with type 2 diabetes after consumption of two different composition breakfasts. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 114(11), 1811–1818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2014.06.352 Corona-Cervantes, K., Parra-Carriedo, A., Hernández-Quiroz, F., Martínez-Castro, N., Vélez-Ixta, J. M., Guajardo-López, D., García-Mena, J., & Hernández-Guerrero, C. (2022). Physical and Dietary Intervention with Opuntia ficus-indica (Nopal) in Women with Obesity Improves Health Condition through Gut Microbiota Adjustment. Nutrients, 14(5), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051008 Bacardi-Gascon, M., Dueñas-Mena, D., & Jimenez-Cruz, A. (2007). Lowering effect on postprandial glycemic response of nopales added to Mexican breakfasts. Diabetes care, 30(5), 1264–1265. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-2506 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Fiber: the carb that helps you manage diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/role-of-fiber.html Remes-Troche, J. M., Taboada-Liceaga, H., Gill, S., Amieva-Balmori, M., Rossi, M., Hernández-Ramírez, G., García-Mazcorro, J. F., & Whelan, K. (2021). Nopal fiber (Opuntia ficus-indica) improves symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome in the short term: a randomized controlled trial. Neurogastroenterology and motility, 33(2), e13986. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13986 National Institutes of Health (NIH). Office of Dietary Supplements. (2024). Calcium. Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-HealthProfessional/ El-Mostafa, K., El Kharrassi, Y., Badreddine, A., Andreoletti, P., Vamecq, J., El Kebbaj, M. S., Latruffe, N., Lizard, G., Nasser, B., & Cherkaoui-Malki, M. (2014). Nopal cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) as a source of bioactive compounds for nutrition, health and disease. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 19(9), 14879–14901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19091487 Onakpoya, I. J., O'Sullivan, J., & Heneghan, C. J. (2015). The effect of cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.), 31(5), 640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2014.11.015 Corona-Cervantes, K., Parra-Carriedo, A., Hernández-Quiroz, F., Martínez-Castro, N., Vélez-Ixta, J. M., Guajardo-López, D., García-Mena, J., & Hernández-Guerrero, C. (2022). Physical and Dietary Intervention with Opuntia ficus-indica (Nopal) in Women with Obesity Improves Health Condition through Gut Microbiota Adjustment. Nutrients, 14(5), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051008
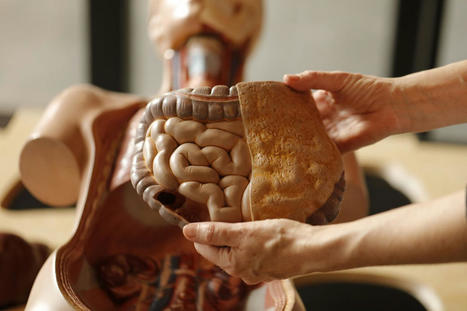
The body needs food for fuel, energy, growth, and repair. The digestive process breaks down food into a form the body can absorb and use for fuel. The broken-down food gets absorbed into the bloodstream from the small intestine, and the nutrients are carried to the cells throughout the body. Understanding how the organs work together to digest food can help with health goals and overall health. The Digestive Process The organs of the digestive system are the following: - Mouth
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Pancreas
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Anus
The digestive process starts with the anticipation of eating, stimulating the glands in the mouth to produce saliva. The digestive system's primary functions include: - Mixing food
- Moving food through the digestive tract - peristalsis
- The chemical breakdown of food into smaller absorbable components.
The digestive system converts food into its simplest forms, which include: - Glucose - sugars
- Amino acids - protein
- Fatty acids - fats
Proper digestion extracts nutrients from food and liquids to maintain health and function properly. Nutrients include: - Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water
Mouth and Esophagus - The food is ground up by the teeth and moistened with saliva to swallow easily.
- Saliva also has a special chemical enzyme that starts breaking down carbohydrates into sugars.
- Muscular contractions of the esophagus massage the food into the stomach.
Stomach - The food passes through a small muscle ring into the stomach.
- It gets mixed with gastric chemicals.
- The stomach churns the food to break it down further.
- The food is then squeezed into the first part of the small intestine, the duodenum.
Small Intestine - Once in the duodenum, the food mixes with more digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver.
- The food passes into the lower parts of the small intestine, called the jejunum and the ileum.
- Nutrients are absorbed from the ileum, lined with millions of villi or thread-like fingers that facilitate the absorption.
- Each villus is connected to a mesh of capillaries, which is how nutrients get absorbed into the bloodstream.
Pancreas - The pancreas is one of the largest glands.
- It secretes digestive juices and a hormone called insulin.
- Insulin helps regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
- Problems with insulin production can lead to conditions like diabetes.
Liver The liver has several different roles that include: - Breaks down fats using bile stored in the gallbladder.
- Processes proteins and carbohydrates.
- Filters and processes impurities, medications, and toxins.
- Generates glucose for short-term energy from compounds like lactate and amino acids.
Large Intestine - A large reservoir of microbes and healthy bacteria live in the large intestine and play an important role in healthy digestion.
- Once the nutrients have been absorbed, the waste is passed into the large intestine or bowel.
- Water is removed, and the waste gets stored in the rectum.
- It is then passed out of the body through the anus.
Digestive System Health Ways to keep the digestive system and the digestive process healthy include: Drink More Water - Water helps the food flow more easily through the digestive system.
- Low amounts of water/dehydration are common causes of constipation.
Add More Fiber - Fiber is beneficial to digestion and helps with regular bowel movements.
- Incorporate both soluble and insoluble fiber.
- Soluble fiber dissolves in water.
- As soluble fiber dissolves, it creates a gel that can improve digestion.
- Soluble fiber may reduce blood cholesterol and sugar.
- It helps your body improve blood glucose control, which can aid in reducing your risk for diabetes.
- Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water.
- Insoluble fiber attracts water into the stool, making it softer and easier to pass with less strain on the bowels.
- Insoluble fiber can help promote bowel health and regularity and supports insulin sensitivity which can help reduce the risk of diabetes.
Balanced Nutrition - Eat fruit and vegetables daily.
- Choose whole grains over processed grains.
- Avoid processed foods in general.
- Choose poultry and fish more than red meat and limit processed meats.
- Cut down on sugar.
Eat Foods with Probiotics or Use Probiotic Supplements - Probiotics are healthy bacteria that help combat unhealthy bacteria in the gut.
- They also generate healthy substances that nourish the gut.
- Consume probiotics after taking antibiotics that often kill all the bacteria in the gut.
Eat Mindfully and Chew Food Slowly - Chewing food thoroughly helps to ensure the body has enough saliva for digestion.
- Chewing food thoroughly also makes it easier for nutritional absorption.
- Eating slowly gives the body time to digest thoroughly.
- It also allows the body to send cues that it is full.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References GREENGARD, H. "Digestive system." Annual review of physiology vol. 9 (1947): 191-224. doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.09.030147.001203 Hoyle, T. "The digestive system: linking theory and practice." British journal of nursing (Mark Allen Publishing) vol. 6,22 (1997): 1285-91. doi:10.12968/bjon.1997.6.22.1285 https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/digestive-disorders/biology-of-the-digestive-system/overview-of-the-digestive-system https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/digestive-system-how-it-works Martinsen, Tom C et al. "The Phylogeny and Biological Function of Gastric Juice-Microbiological Consequences of Removing Gastric Acid." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 20,23 6031. 29 Nov. 2019, doi:10.3390/ijms20236031 Ramsay, Philip T, and Aaron Carr. "Gastric acid and digestive physiology." The Surgical clinics of North America vol. 91,5 (2011): 977-82. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2011.06.010
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...








Learn how to promote gut healing after food poisoning. Discover the foods and drinks that can help your body recover and feel better faster. For answers to any questions you may have, call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900 or 915-412-6677